Fig. 5.
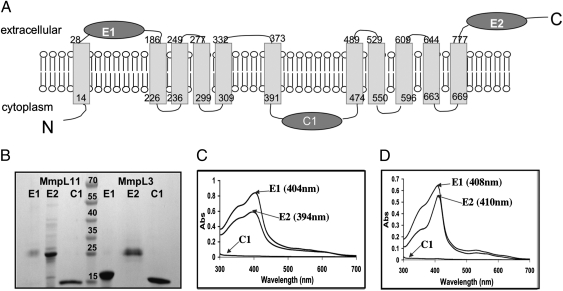
Examination of heme binding capabilities of the predicted soluble domains of MmpL11 and MmpL3. (A) Predicted topology of MmpL11 (Rv0202c), which is very similar to that of MmpL3 (Rv0206c), Fig. S4H. There are 11 transmembrane helices, two extracellular domains (E1 and E2), and one cytoplasmic domain (C1). (B) SDS/PAGE of purified domains of both MmpL11 and MmpL3. Domains of MmpL11 are to the left of the lane with molecular weight markers and domains of MmpL3 are to the right of the lane with molecular weight markers (kDa), as indicated. (C and D) UV/vis absorbance spectra of domains E1, E2, and C1 from MmpL11 (C) and MmpL3 (D) after each domain was incubated with heme and repurified by gel filtration. For both MmpL11 and MmpL3, both E1 and E2 bind heme whereas C1 does not.