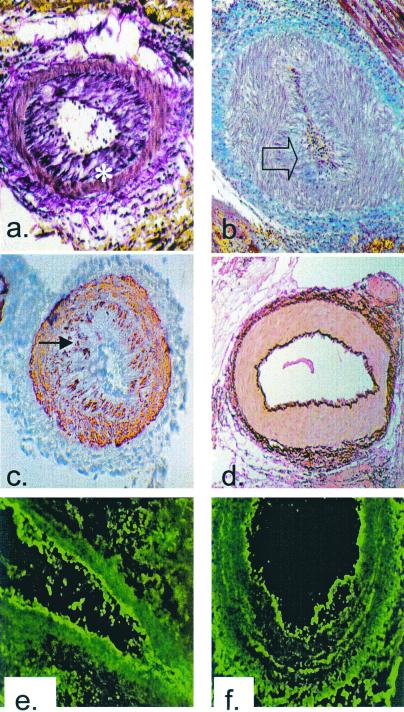
Figure 1.
Histological analysis of cardiac allografts. (a)
Voerhoeff elastin stain of the rejected cardiac allograft from
recipient no. 13511 on POD 5 (×100). Asterisk indicates internal
elastic lamina. (b) Trichrome stain of the rejected
cardiac allograft from recipient no. 13692 on POD 5 (×100). Blue
staining indicates the presence of collagen within occluding neointima,
as indicated by transparent arrow. (c) α-Actin
staining of the rejected cardiac allograft from recipient no. 13692 on
POD 5 showing smooth muscle cell accumulation within the intima,
indicated by filled arrow (×100). (d) Voerhoff elastin
stain of cardiac allograft from DRβ control pig no.
13914 at POD 15 showing no intimal thickening (×100).
(e) Immunofluorescent staining for IgM on the rejected
cardiac allograft from recipient no. 13692 on POD 5 showing antibody
deposition along the arteriolar endothelium (×250).
(f) Immunofluorescent staining for IgG on the
rejected cardiac allograft from recipient no. 13692 on POD 5 showing
antibody deposition along arteriolar endothelium (×250). Naïve
control hearts did not stain for antibody.
control pig no.
13914 at POD 15 showing no intimal thickening (×100).
(e) Immunofluorescent staining for IgM on the rejected
cardiac allograft from recipient no. 13692 on POD 5 showing antibody
deposition along the arteriolar endothelium (×250).
(f) Immunofluorescent staining for IgG on the
rejected cardiac allograft from recipient no. 13692 on POD 5 showing
antibody deposition along arteriolar endothelium (×250). Naïve
control hearts did not stain for antibody.