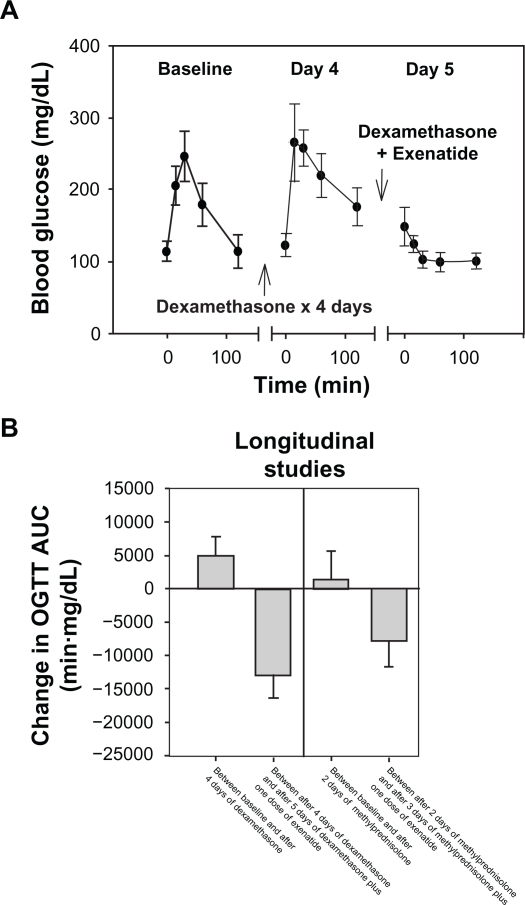
Figure 1.
Exenatide suppressed the rise in blood glucose after an oral glucose load in mice with glucocorticoid-induced glucose intolerance. A) Average blood glucose levels of nine adult C57BL/6 mice during an OGTT performed on three occasions are plotted against time. The error bars represent 95% CI. After baseline OGTT, each mouse was injected dexamethasone (20 mg/kg/day) IP for 4 days. The day 4 OGTT was performed several hours after dexamethasone injection in the morning. On day 5, the OGTT was performed after injection of dexamethasone IP and exenatide (3 μg/kg) SQ. B) The average change in AUC between the first and second OGTT of each mouse and between the second and third OGTT are plotted in the left panel for the longitudinal experiment described in A. Similar data for a separate experiment using a less potent glucocorticoid (methylprednisolone) and shorter duration than in A) are plotted in the right panel. The error bars represent 95% CI.
Abbreviations: AUC, area under the curve; CI, confidence intervals; IP, intraperitoneal; OGTT, oral glucose tolerance test.