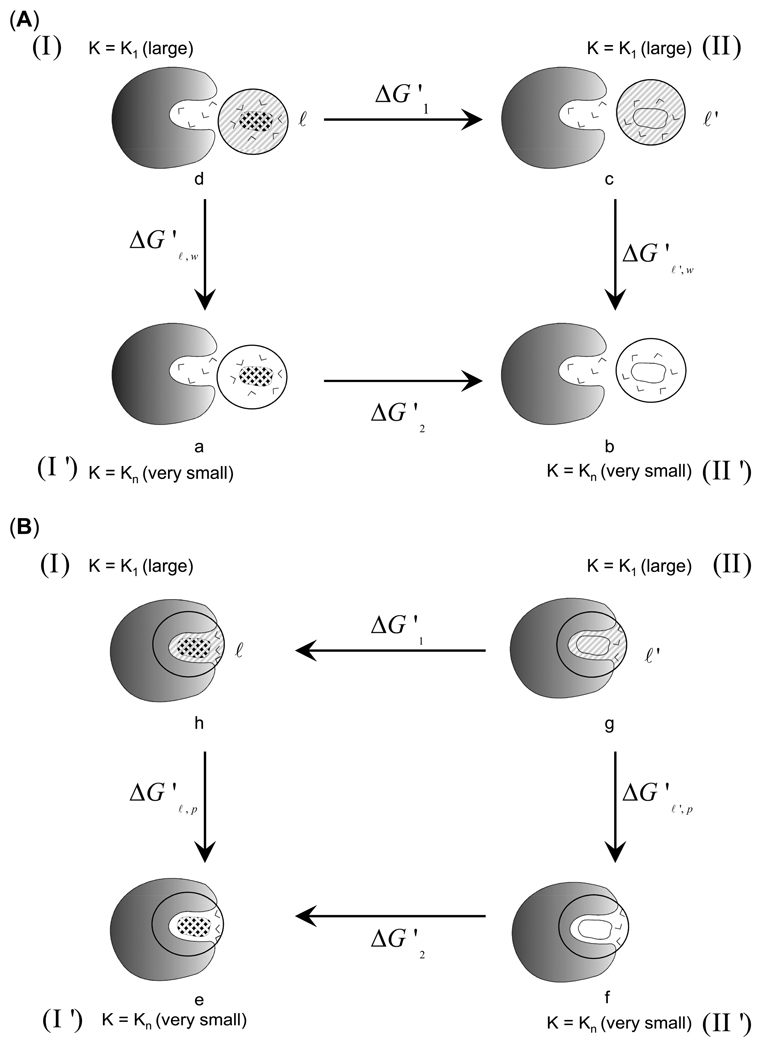
Figure 3.
The thermodynamics cycles for the calculation of the entropy loss upon ordering of the solvent molecules in the vicinity of a charged solute. The shaded area designates large constraint and fixed solvent whereas the white areas designates free solvent molecules. (A) The cycle (a→b→c→d) provides the polarization entropy in water (). (B) The cycle (e→f→g→h) provides the corresponding entropy contribution in protein (). The difference between the entropy values obtained from the two cycles provide the overall entropy loss due to the electrostatically-induced ordering of solvent molecules upon moving the solute (ℓ) from water to the protein ().