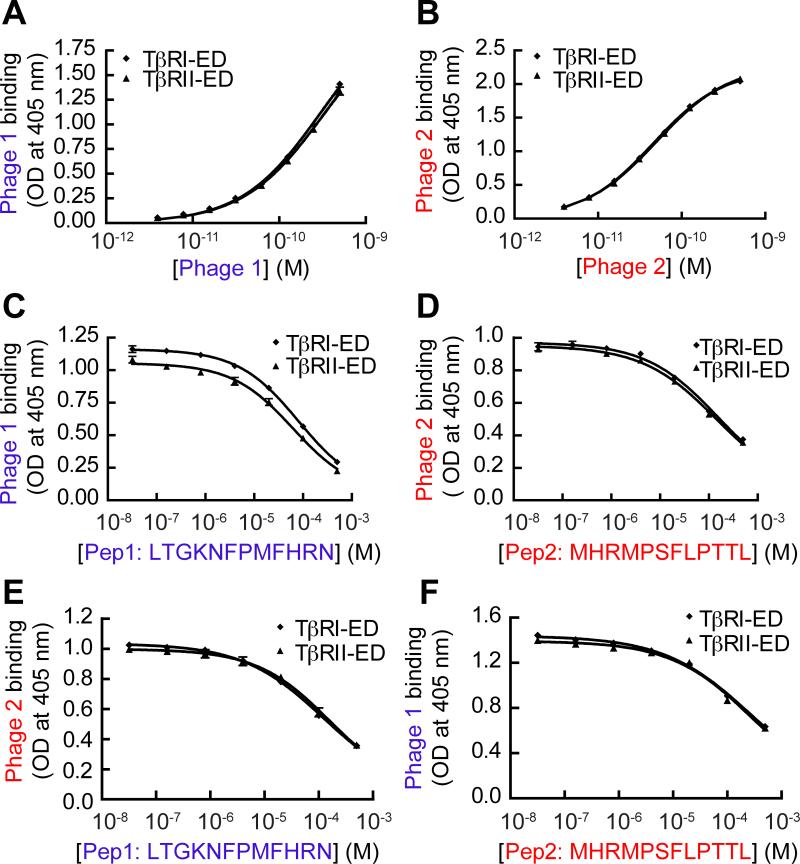
FIG. 2.
Phage display against TβRI yields peptides that bind TβRI-ED and TβRII-ED indistinguishably. The binding of (A) phage clone 1 and (B) phage clone 2 to immobilized TβRI-ED and TβRII-ED was assessed using a phage-based ELISA. (C) ELISA-based competition binding assay. Pep1 derived from phage clone 1 and (D) Pep2 derived from clone 2 were tested for inhibition of phage clone binding to immobilized receptors (550 pM of clone 1 and 39 pM of clone 2 were used). (E) An assay with Pep1competing with phage clone 2 (39 pM) for binding to either immobilized TβRI-ED or TβRII-ED. The IC50 value for Pep1 with phage clone 2 and TβRI-ED is 110 μM; the corresponding value for TβRII-ED is 156 μM. (F) An assay with Pep2 competing with phage clone 1 (550 pM) for binding to either immobilized TβRI-ED or TβRII-ED. The IC50 value for Pep2 inhibiting phage clone 1 binding to TβRI-ED is 256 μM; the corresponding value for TβRII-ED is 274 μM. Error bars represent the mean ± the standard deviation in (A) to (F).