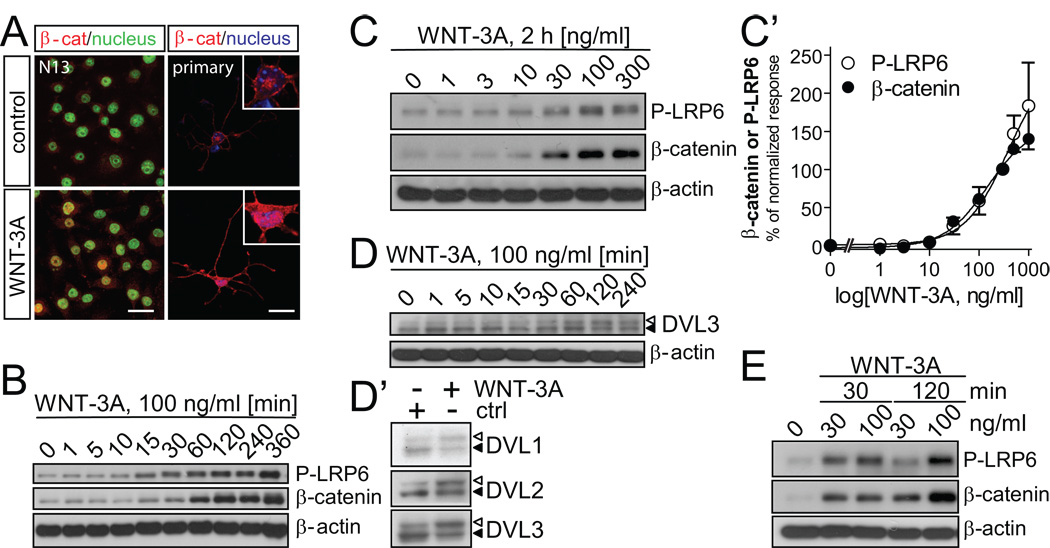
Fig. 6. WNT-3A induces WNT/β–catenin signaling in microglia cells.
(A) β-catenin localization in N13 and primary mouse microglia cells in combination with SYTOX Green (N13) or DAPI (primary microglia) as nuclear counterstain. Confocal laser-scanning photomicrographs were captured in control and WNT-3A-stimulated (100 ng/ml, 2h) cells. Scale bar = 20 µm. (B) WNT-3A induces LRP6 phosphorylation (P-LRP6) and β-catenin stabilization over time in N13 cells and (C) with increasing concentrations (2 h). P-LRP6, β-catenin and β-actin levels were monitored by immunoblotting. (C’) A dose-response curve was constructed where each data-point represents the mean ± SEM from n=4 – 6 independent observations/data point. P-LRP6 and β–catenin levels in control (ctrl) were set to zero while response to 300 ng/ml of WNT-3A was considered 100%. (D) WNT-3A stimulation for 2h activates DVL1, 2, 3 isoforms visualized by electrophoretic mobility shift (PS-DVL is indicated by open triangle; non-shifted DVL form is marked with filled triangle). (E) Dose- and time-dependence of P-LRP6 and β-catenin levels in primary mouse microglia with β-actin as loading control.