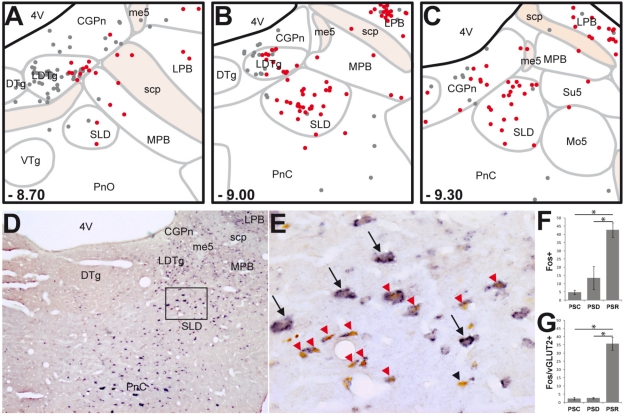
Figure 1.
SLD neurons expressing Fos after PS-recovery are mostly glutamatergic. (A-C) Schematic distribution of Fos+ (gray dots) and Fos-vGLUT2+ (red dots) neurons on coronal sections taken at 300 μm intervals through the full rostro-caudal extent of the SLD in a representative PSR animal. Rostro-caudal localization of each section is indicated from Bregma at the bottom left corner of each drawing. (D-E) Photomicrographs showing Fos (brown nuclear staining) and vGLUT2 (blue diffuse cytoplasmic staining) double staining at SLD level. (E) is a higher magnification of the rectangular box in D. Note the dense cluster of double-labeled neurons into the SLD of a PSR rat. Interestingly, most of the large glutamatergic SLD neurons do not express Fos after PS hypersomnia (black arrows). Conversely, double-labeled neurons after PS hypersomnia are rather of small size (red arrowheads). Only one neuron labeled for Fos after PS-hypersomnia does not express vGLUT2 mRNA (black arrowhead). (F-G) Number of Fos+ and Fos/vGLUT2+ neurons in the SLD in control (PSC), PS deprived (PSP) and PS recovery (PSR) conditions. Values are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05. 4V, 4th ventricle; CGPn, central gray of the pons; DTg, dorsal tegmental nucleus; LDTg, laterodorsal tegmental nucleus; LPB, lateral parabrachial nucleus; me5, mesencephalic trigeminal tract; Mo5, motor trigeminal nucleus; MPB, medial parabrachial nucleus; PnC, pontine reticular nucleus, caudal part; PnO, pontine reticular nucleus, oral part; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; SLD, sublaterodorsal tegmental nucleus; su5, supratrigeminal nucleus; VTg, ventral tegmental nucleus.