Fig. 4.
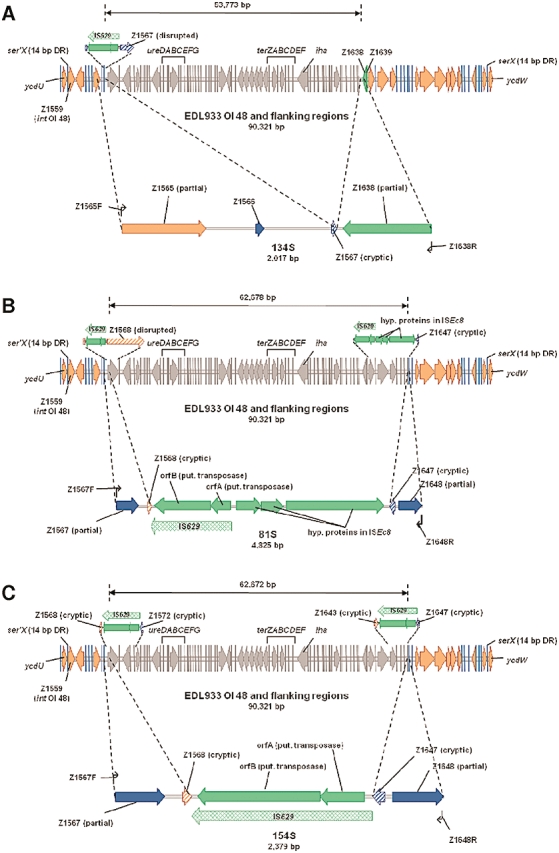
Deletions of OI 48 in strains 134S (A), 81S (B) and 154S (C). The upper part in each illustration shows the organization of OI 48 and its flanking regions in reference E. coli O157:H7 strain EDL933. Insertions of novel IS elements in the respective L strains are depicted above the island. The solid line above the genetic map depicts the extent of internal deletions in the three S strains (depicted in grey in the EDL933 sequence). In the lower part, the size (given in bp below the strain number) and genetic organization of the connecting fragment amplified after deletion of an internal part of OI 48 in each respective strain is shown (not drawn to scale). Small arrows symbolize primer binding sites for amplification of the connecting fragment (PCR primers and conditions are in Table S1). Outer dotted lines indicate homologies between OI 48 of EDL933 and the amplification product. The green arrows between the inner dotted lines depict sequences replacing the deleted region (IS, insertion sequence; hyp., hypothetical; put., putative). Indicated genes of OI 48 and flanking regions are int (putative P4-family integrase), ure (urease) and ter (tellurite resistance) clusters, iha, ORFs relevant to the deletion analyses, serX/ser'X (intact/cryptic tRNA gene) including direct repeats (DR) flanking the OI and ycdU/ycdW (chromosomal genes).
