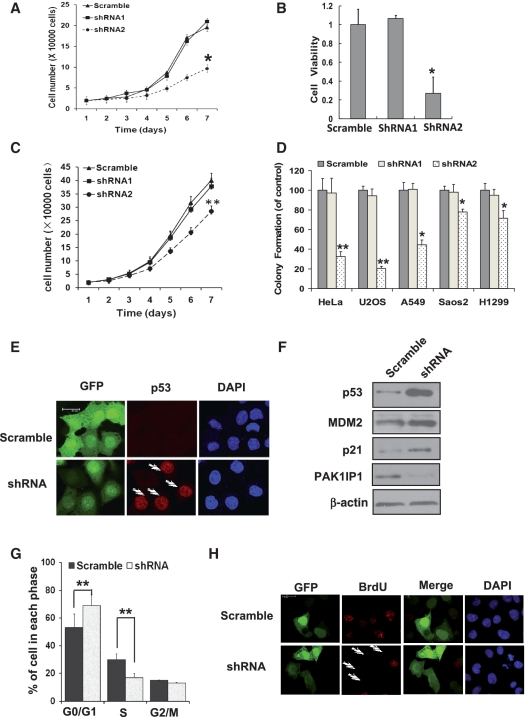
Figure 6.
Knockdown of PAK1IP1 inhibits cell proliferation with p53 activation. (A, B and C) Knockdown of PAK1IP1 inhibits cell growth and viability. Cell growth curves of HeLa (A) and H1299 (C) cells, infected with the indicated lentivirus, were determined from Day 1 to Day 7 after infections. The same number of infected cells was seeded in 24-well plates to grow for 1–7 days and the cell number was counted every day. The number of viable cells in HeLa cells was measured by MTS (B). (D) Knockdown of PAK1IP1 reduces the efficiency of colony formation in p53 positive and negative cells. Indicated cells were infected with scramble or PAK1IP1 shRNA lentiviruses (shRNA1 or shRNA2) and seeded into 33-mm dish with 1000 cells. After a 14-day growth, the numbers of colonies were counted as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section. Data was representative of three independent experiments (n = 3), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to scramble RNA-infected cells. (E) Knockdown of PAK1IP1 upregulates p53 protein level. HeLa cells were infected with indicated lentiviruses for 48 h. GFP and p53 were detected by immunostaining with confocal laser scanning microscopy. The arrows showed that the p53 protein was accumulated in GFP-positive cells indicating the knockdown of PAK1IP1. (F) Down-regulation of PAK1IP1 increased protein level of p53 and its target proteins, MDM2 and p21. (G) Knockdown of PAK1IP1 induces G1/S cell-cycle delay. HeLa cells were infected with the indicated lentiviruses for 48 h. Cell-cycle distributions were analyzed by FACS analysis. (H) Knockdown of PAK1IP1 inhibits BrdU incorporation. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 48 h and then BrdU was supplemented. After 10 h, the cells were immunostained with BrdU specific antibody (red) and the nucleus was stained with DAPI. The arrows showed the GFP-positive cells with undetectable BrdU incorporation. Bars, 20 μm.