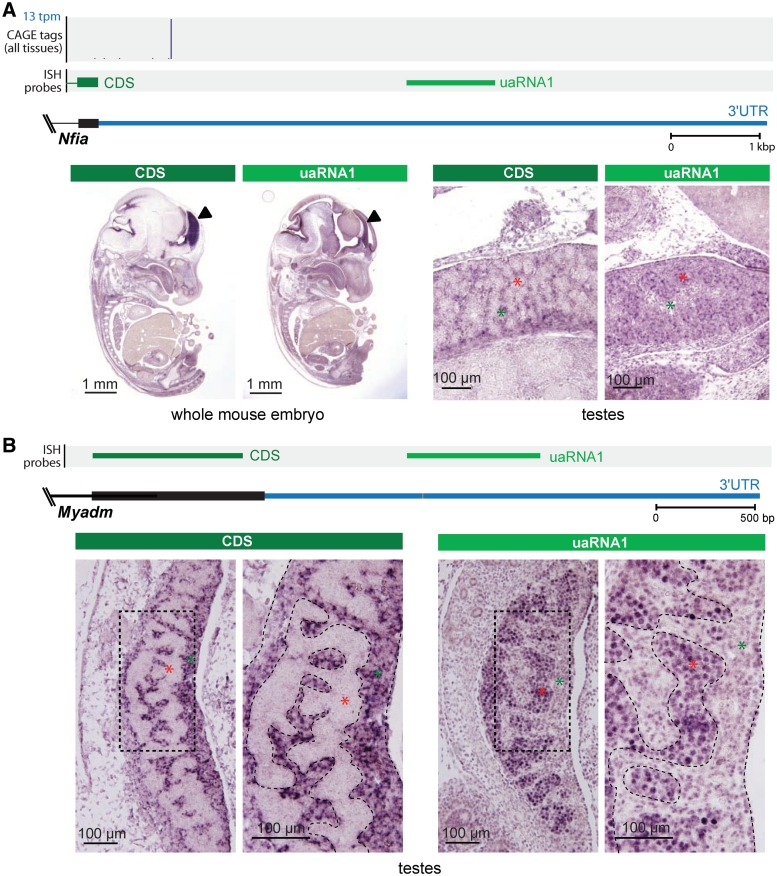
Figure 5.
uaRNAs within the Nfia and Myadm 3′UTRs. (A) (Top panel) Genomic context of Nfia 3′UTR showing annotated coding sequence (CDS, black) and 3′UTR (blue), histogram of CAGE distribution and density (tpm, tags per million), and riboprobes used in ISH that target the terminal constitutive coding exons (dark green; CDS) and 3′UTR (light green; uaRNA1). (Bottom panel) Section ISH showing the Nfia CDS probe detecting expression in interstitial cells (green asterisks) of 12.5 dpc testes (marker) and the uaRNA probe detecting expression within the testis cords (red asterisks). (B) (Top panel) Genomic context of Myadm 3′UTR showing annotated coding sequence (CDS, black) and 3′UTR (blue), riboprobes used in ISH that target the terminal constitutive coding exon (dark green; CDS) and 3′UTR (light green; uaRNA1). (Bottom panel) Section ISH showing the Myadm CDS probe detecting expression in the cytoplasm of interstitial cells (green asterisks) in the developing testis at 12.5 dpc and the uaRNA probe detecting expression in the nuclei of Sertoli cells and germ cells in the testis cords (red asterisks). High Myadm expression was not detected by either the CDS or the uaRNA probe elsewhere in the embryo (see Supplementary Figure S8).