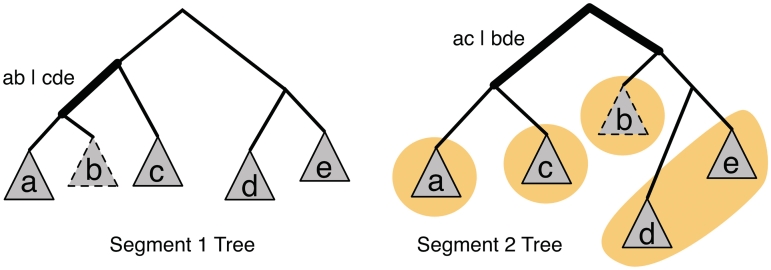
Figure 2.
Reassortment candidates. The pair of incompatible splits in the two segment trees define four candidate sets (obtained by computing intersections, {a, b}∩{a, c} = {a}, {a, b} ∩ {b, d, e} = {b}, {c, d, e} ∩ {a, c} = {c} and {c, d, e} ∩ {b, d, e} = {d, e}), one of which is the reassortment set ({b}). The set {b} also satisfies the condition that it is similar to some taxa and more diverged with respect to others when comparing the two segment trees. Note that set {d} also has this property, demonstrating that it is not a sufficient condition for identifying a reassortment.