Figure 5.
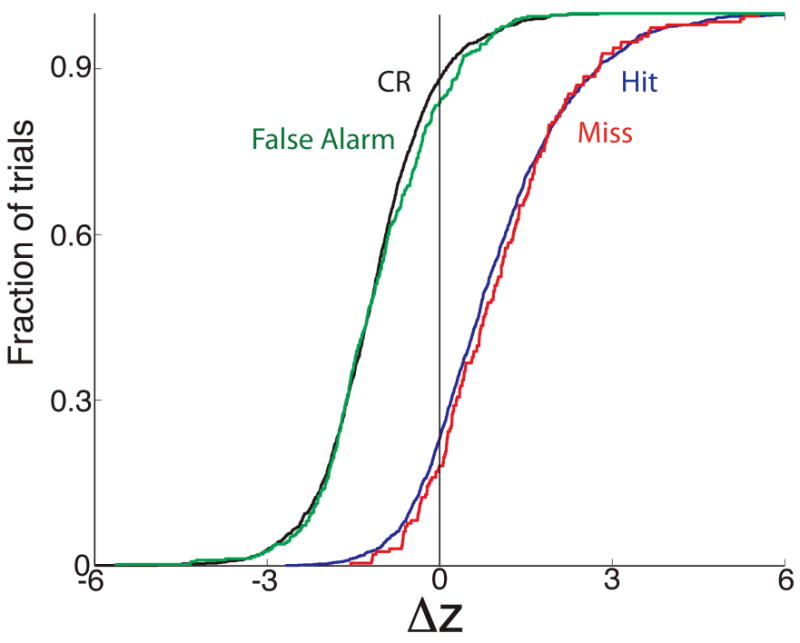
Cumulative histograms of the responses of synchronized firing of pairs of multi-units to odors in the odor discrimination task shown separately for trials where the animal makes the correct behavioral decision (hits, blue and correct rejections, CR, black) or an incorrect decision (false alarm in green and miss in red). Responsiveness was calculated on a trial-per-trial basis in divergent blocks that included at least one mistake as a z-score defined in the Methods. A positive z-score indicates that the synchronized firing rate increased upon exposure to the odor. An ANOVA with a post-hoc test indicated that the z-scores for miss were not different from the z-scores for hits and that the responses from false alarms did not differ from correct rejections. There was a significant difference between hits/misses and correct rejections/false alarms. In order to ensure the incorrect trials mirrored the correct trials we also did an ANOVA where we only included false alarms where the animal licks for 80% or more of the time in the 2 sec response area and misses where the animal licked less than 20% of the time in the response area. The ANOVA test yielded the same differences/lack of differences between hits, misses, correct rejections and false alarms. The number of trials included are: 1,431 hits, 193 misses, 1,219 correct rejections and 378 false alarms.
