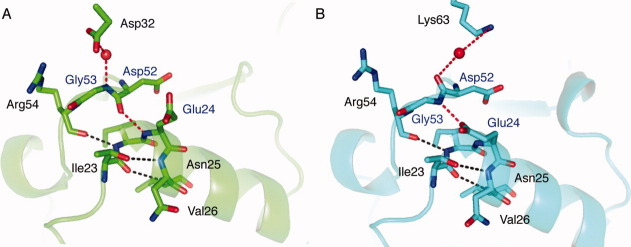
Figure 2.
The two ubiquitin structures [1UBQ (green) and our new structure (cyan)] have different hydrogen bonds capping the N-terminal α-helices (shown in red) and crystal contacts. (A) The Asp52 carbonyl of 1UBQ forms an internal hydrogen bond with backbone of Glu24. Gly53 forms an intermolecular hydrogen bond with Asp32 of a neighboring ubiquitin molecule. (B) The Gly53 amide of our new ubiquitin structure forms an internal hydrogen bond with the Glu24 side chain; the Asp52 carbonyl forms an intermolecular hydrogen bond with Lys63 of a neighboring ubiquitin molecule through a water molecule.