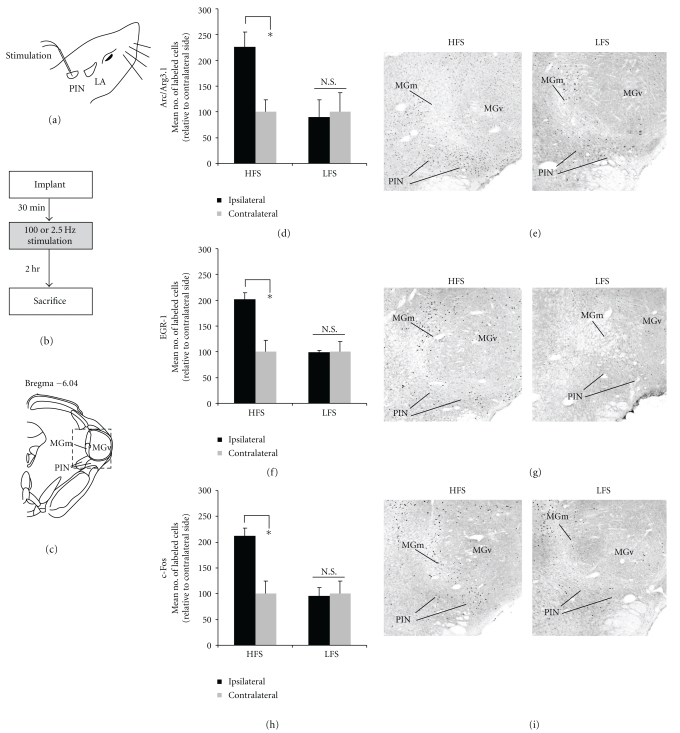
Figure 4.
High-frequency stimulation of the MGm/PIN promotes increased immunolabeling of ERK-driven IEGs in the MGm/PIN. (a) Placement of stimulation electrode. (b) Schematic representation of experimental protocol. Rats were given HFS or LFS and sacrificed 2 hours after stimulation. (c) Schematic representation of the auditory thalamus at Bregma –5.6. (d) Mean (±SEM) percent Arc/Arg3.1 immunoreactive cells in the MGm/PIN from rats receiving HFS (n = 6) or LFS (n = 6). (e) Photomicrographs showing Arc/Arg3.1-labeled cells from rats receiving HFS (left) or LFS (right). (f) Mean (±SEM) percent EGR-1 immunoreactive cells in the MGm/PIN from rats receiving HFS (n = 6) or LFS (n = 6). (g) Photomicrographs showing EGR-1-labeled cells from rats receiving HFS (left) or LFS (right). (h) Mean (±SEM) percent c-Fos immunoreactive cells in the MGm/PIN from rats receiving HFS (n = 6) or LFS (n = 6). (i) Photomicrographs showing c-Fos-labeled cells from rats receiving HFS (left) or LFS (right). In each experiment, ipsilateral cell counts have been expressed as a percentage of contralateral cell counts for each rat. *P < .05 relative to the ipsilateral side N.S. = not significant. MGm = medial division of the medial geniculate nucleus; MGv = ventral division of the medial geniculate nucleus; PIN = posterior intralaminar nucleus.