Fig. 1.
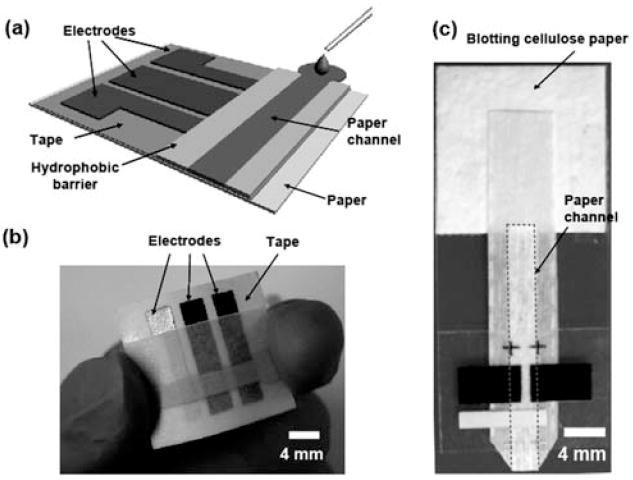
(a) Schematic of a paper-based electrochemical sensing device. The sensor comprises three electrodes printed on a piece of paper substrate (or plastic) and a paper channel. The paper channel was in conformal contact with the electrodes, and was held in place by double-sided adhesive tape surrounding the electrodes. A photograph of a paper-based electrochemical sensing device for the analysis of glucose (b), and a hydrodynamic paper-based electrochemical sensing device for the measurement of heavy-metal ions (c). The device consists of two printed carbon electrodes as the working and counter electrodes, and a printed Ag/AgCl electrode as the pseudo-reference electrode. The paper channel was fabricated by patterning SU-8 as a hydrophobic barrier for aqueous solution. The paper channel in (b) was colored with red ink to enhance imaging. The dashed line in (c) indicates the edge of the paper channel. The scale bar is 4 mm.
