Fig. 4.
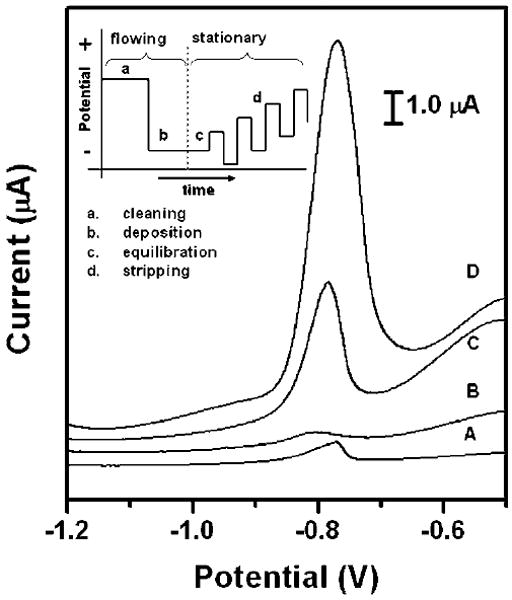
Square-wave anodic stripping voltammograms for 25 ppb solution of Pb(ii) in 0.1 M acetate buffer (pH 4.5) in the presence of 25 ppb Zn(ii) : (A) a 100 μL solution placed directly on the electrodes; (B) a 100 μL solution added to the stagnant μPEDs (without a pad of blotting paper as sink); (C and D) a solution of analytes continuously wicking the paper channel of the hydrodynamic μPEDs. The deposition time was 120 s (A, B, C) or 360 s (D). The SWASV was performed in the potential range of −1.2 to −0.5 V under optimized conditions: frequency, 20 Hz; amplitude, 25 mV; potential increment, 5 mV; equilibration time, 30 s. Deposition was performed at −1.2 V; ‘cleaning’ was performed at +0.5 V for 60 s. A bismuth(iii) concentration of 500 μg L−1 was chosen for the co-deposition of heavy-metal ions. We used screen-printed carbon electrodes as the working and counter electrodes, and a screen-printed Ag/AgCl electrode as the reference electrode. Inset shows the schematic of the four steps of the square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry.
