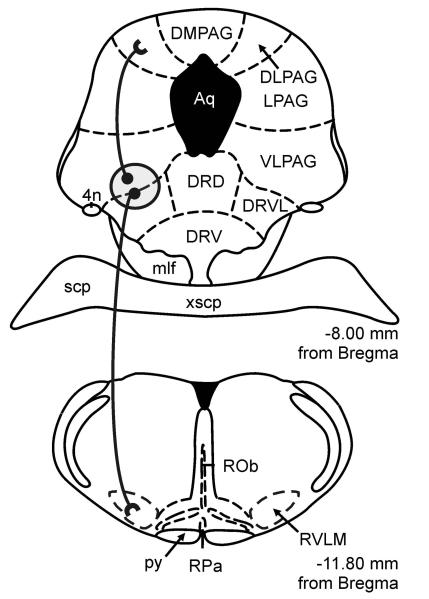
Figure 4.
Proposed periventricular serotonergic path, arising from the DRVL/VLPAG region, as part of a sympathomotor control system. Serotonergic neurons in the DRVL/VLPAG region project, via monosynaptic pathways, to the DLPAG region involved in panic-like behavioral responses to aversive stimuli and to the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) involved in stress-induced hypertension and sympathetic activation (Johnson et al., 2004). Serotonergic neurons in the DRVL/VLPAG region project, via multisynaptic pathways, to both the adrenal gland and skeletal muscle (Kerman et al., 2006), providing an anatomical substrate for synchronized control of both autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or panic-inducing stimuli. For functional topography of serotonergic systems, see reviews (Graeff et al., 1997; Lowry, 2002; Johnson et al., 2004). Circle with gray shading indicates the DRVL/VLPAG region containing serotonergic neurons activated by sodium lactate infusions in control rats, but not in anxious, panic-prone rats with inhibition of GABAergic tone in the dorsomedial hypothalamus. Abbreviations: 4n, trochlear nerve; DLPAG, dorsolateral periaqueductal gray; DMPAG, dorsomedial periaqueductal gray; LPAG, lateral periaqueductal gray; py, pyramidal tract; ROb, raphe obscurus nucleus; RPa, raphe pallidus nucleus; RVLM, rostral ventrolateral medulla; scp, superior cerebellar peduncle; xscp, decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle. For additional abbreviations, see Figure 1 legend.