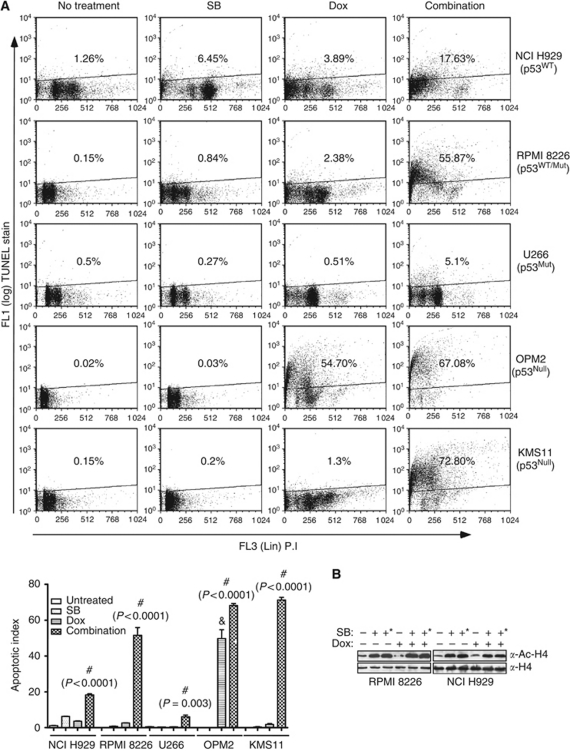
Figure 1.
Combinations of HDACi and doxorubicin potentiate apoptosis in myeloma cells. (A) Effects of HDACi, doxorubicin and their combination on apoptosis of myeloma cells with varying p53 status. Myeloma cells (1 × 106) carrying either wild-type or mutant p53 (NCI H929, RPMI 8226, U266, KMS11 and OPM2) were left untreated or treated with butyrate (300 μM for NCI H929 and 600 μM for RPMI 8226, U266, KMS 11 and OPM2) or doxorubicin (40 nM) or with their combination for 48 h. Percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining. Scatter plot shown is a representative of two independent experiments with similar results, in which 10 000 events were collected using flow cytometry. Mutational status of p53 of the myeloma cell lines is indicated. Induction of apoptosis in myeloma cells by butyrate, doxorubicin and their combination are summarised in the bottom graph. Each bar on the graph is mean±s.e.m. of two independent experiments. # Indicates that the treatment is significantly different from other treatments and ‘&’ sign indicates that treatment is significantly different from untreated or butyrate treatment; P-values for each treatment is provided. (B) Effect of butyrate and doxorubicin (40 nM) combination on HDAC activity. Whole-cell lysates (WHL; 30 μg) of NCI-H929 or RPMI 8226 cells left untreated or treated with butyrate (+=300 μM, +*=600 μM) doxorubicin or their combination for 36 h and acetylation status of histone H4 as an indirect measure of HDAC activity was determined by immunoblot analysis.