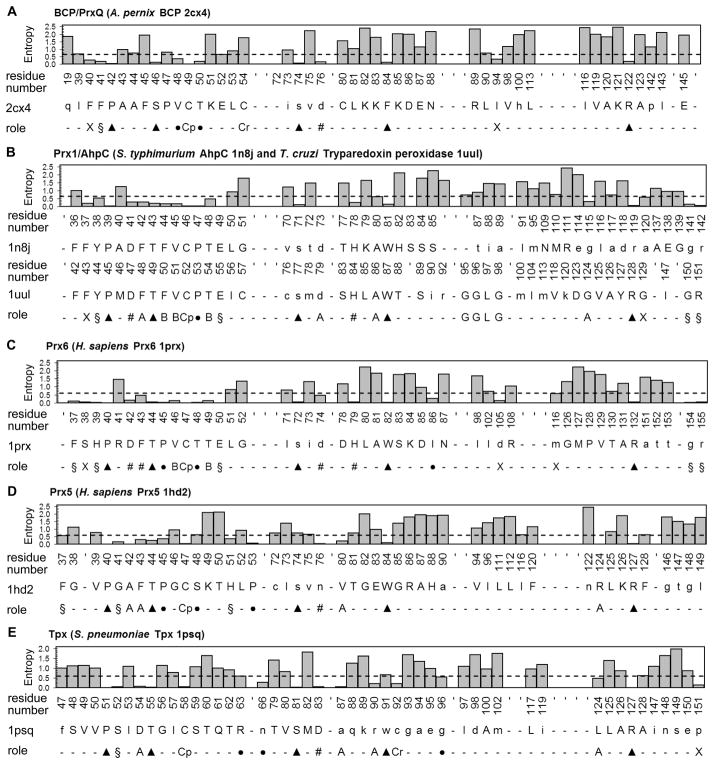
Figure 3. Residue conservation and potential structural/functional role for each residue in Prx subfamily functional site profiles.
The functional site signatures are shown for a representative member of each of the Prx subfamilies. The degree of conservation is shown for each residue after aligning the full sequence for all of the putative members identified from the GenBank(nr) database searches. The actual residues and numbers listed are for (A) Aeropyrum pernix BCP (2cx4), (B) Salmonella typhimurium AhpC (1yep) and Trypanosoma cruzi tryparedoxin peroxidase (1uul), (C) Homo sapiens Prx6 (1prx), (D) H. sapiens Prx5 (1hd2), and (E) Streptococcus pneumoniae Tpx (1psq). Residues with an entropy value below 0.61 (mean minus 1 standard deviation) are considered conserved (dashed line). The potential role for each conserved residue is also represented in the histogram and labeled as follows: the peroxidatic cysteine (Cp), the resolving cysteine (Cr), key residues conserved across all Prx subfamilies (▲), residues involved in forming the active site pocket of the reduced protein (§), residues found in the A-type interface (A), residues found in the B-type interface (B), residues involved in stabilizing the helix containing the CP (●), residues forming a series of H-bonds between the key Thr residue and the region containing the A-type interface (#), and conserved residues that do not fall into any of these groups (X). Hydrogen bonds were analyzed using LIGPLOT 80.