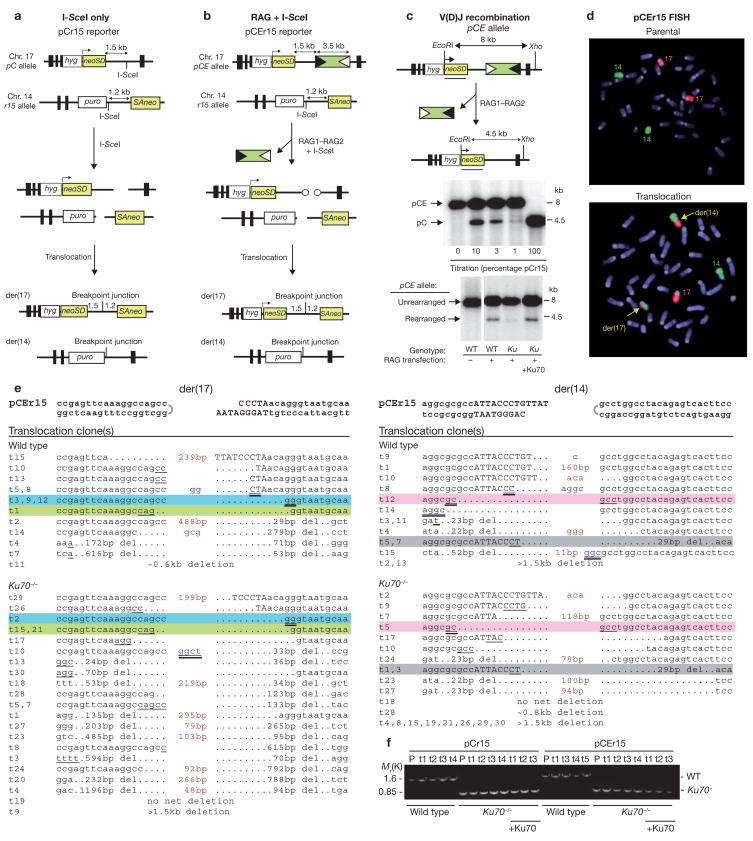
Figure 1.
Chromosomal translocations induced after DSB formation and NHEJ repair. (a) Translocation reporter pCr15. DSB formation at the I-SceI sites on chromosomes 17 and 14, followed by interchromosomal NHEJ, results in a chromosomal translocation and a neo+ gene on der(17) if joining occurs within the 2.7 kb neo intron. The non-palindromic I-SceI sites are present in opposite orientation, such that cleavage results in non-overlapping four-base 3# overhangs. (b) Translocation reporter pCEr15. RAG-recombinase cleavage to generate hairpin ends on chromosome 17 and I-SceI cleavage at the I-SceI site on chromosome 14, followed by interchromosomal NHEJ, results in a chromosomal translocation, similar to pCr15. Circles, hairpin ends; white triangles, 12-RSS; black triangles, 23-RSS. (c) V(D)J recombination at the pCE allele after RAG-recombinase expression. Compared to wild-type cells, V(D)J recombination is significantly reduced in Ku70−/− cells, but is restored by Ku70 expression. V(D)J recombination frequency was quantified by comparison with a standard curve established by diluting known quantities of DNA from cells containing the pCEr15 (8 kb) and pCr15 (4.5 kb) reporters. (d) Fluorescence in situ hybridization. Parental pCEr15 cells have normal chromosomes 14 (green) and 17 (red), whereas neo+ clones, as Ku70−/− clone t1 shown here, also have derivative chromosomes (yellow arrows). (e) Translocation junctions derived from the pCEr15 reporter. Junctions that occurred in both wild-type and Ku70−/− cells are highlighted with the same colour. Deletions that were not confirmed by sequencing are estimates based on Southern blotting. Hairpin ends (half circle), I-SceI site (capital letters), microhomology (underlined), insertions (red), and P nucleotides (blue) are indicated. Possible microhomologies from hairpin opening are double underlined. Long insertions include chromosome 17 RSS–spacer sequences (wild-type der(14)t1; Ku70−/− der(14)t7, der(17)t29; see Supplementary Information, Fig. 1b) and chromosome 14 sequences located within a few kilobases of the DSB which may have been templated (wild-type der(17)t15; Ku70−/− der(17)t1, t18, t20). Smaller templated insertions (<5 bp) are also possible (for example, wild-type der(14)t10). (f) Confirmation of the Ku70 genotype in parental (P) and multiple translocation clones (t). +Ku, Ku70 transient complementation.