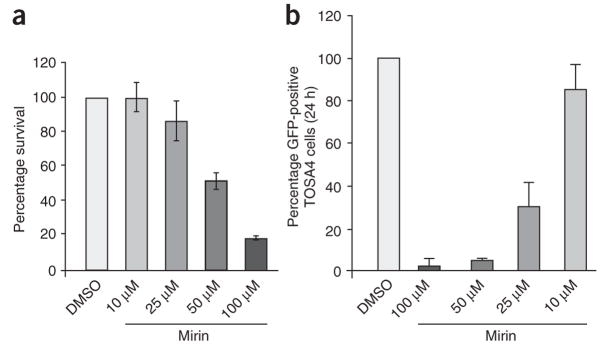
Figure 5.
Mirin inhibits homology-dependent DNA repair in human cells. (a) Cytotoxicity of mirin in HEK293 cells. HEK293 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of mirin, then fixed and stained 10 d later (see Methods). Stained plates were counted for colonies. Percentage survival is expressed as the average number of colonies on treated plates divided by the average number of colonies on control plates (0 μM mirin). Each bar represents an average of three independent experiments with s.d. shown. (b) Gene conversion assay. TOSA4 cells treated with DMSO or mirin at the indicated concentrations were transfected with I-Sce1–expressing plasmid. After 24 h, GFP-expressing cells were then scored by cell sorting. The average of four independent experiments is shown. Each bar represents an average of five independent experiments with s.d. shown.