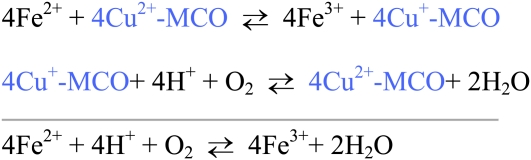Figure 1.
Ferroxidase activity of MCO. Ferrous iron transfers electrons to the Type 1 copper binding site and ferric iron is produced. The cuprous ion is reoxidized by losing electrons to molecular oxygen bound at the Type 2 and Type 3 copper centers. The net result of catalysis is oxidation of ferrous iron and reduction of oxygen to produce ferric iron and water. Ferric iron can then bind transferrin.