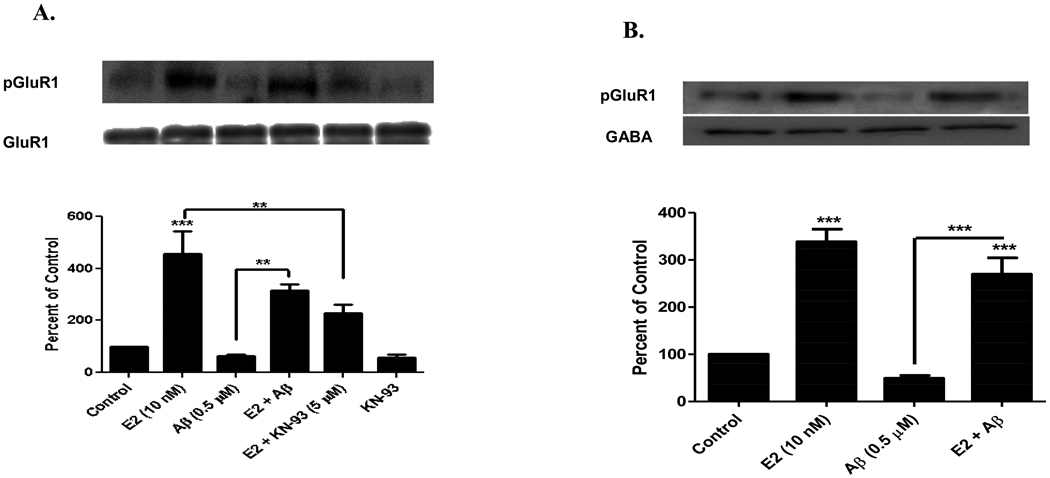
FIGURE 3. E2 Ameliorates Aβ-induced Inhibition of GluR1 Phosphorylation and Decreased GluR1 Membrane Insertion.
A) E2 ameliorates Aβ-induced inhibition of GluR1 phosphorylation in primary cortical neurons. Primary cortical neurons (E18) were grown 15 DIV and were pretreated with soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers (0.5 µM) for 24 hrs. Neurons were then treated with or without E2 (10 nM) for 1 hr in the presence or absence of KN-93. Aβ treatment decreased GluR1 phosphorylation (63 ± 10%), while E2 ameliorated Aβ’s effect (317 ± 38%). E2-induced phosphorylation was inhibited by KN-93 (218 ± 55%). B) GluR1 insertion into the membrane of primary cortical neurons. Primary cortical neurons (E18) were grown 15 DIV and were pretreated with soluble Aβ1–42 oligomers (0.5 µM) for 24 hrs. E2 (10 nM) treatment for 1 hr increased surface expression of pGluR1 (serine 831) and Aβ treatment inhibited this surface expression (338 ± 46% and 49 ± 10%, respectively). The surface expression of pGluR1 (serine 831) was normalized with surface expression of GABA receptor. E2 treatment ameliorated Aβ-induced inhibition of GluR1 insertion into the membrane of cortical neurons (270 ± 17%). Data are mean ± SD. **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.001, versus control or groups connected by bars as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls Multiple Comparison Test, n=3 (3 independent experiments).