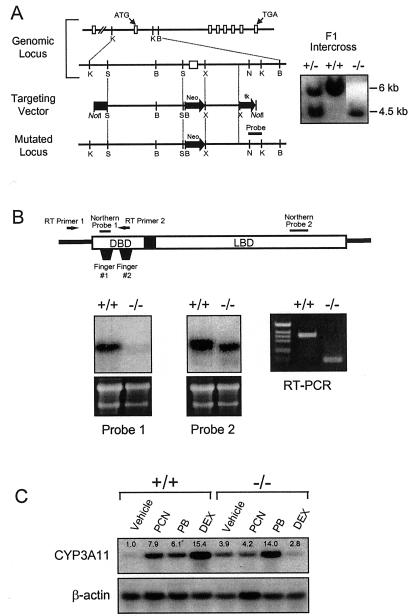
Figure 1.
Disruption of the PXR gene in ES cells and mice. (A) Schematic representation of the PXR locus segment, the targeting vector and the targeted PXR allele. Open boxes indicate exons and labeled boxes indicate the PGK-tk and PGK-neo cassettes. Selected restriction endonuclease sites are indicated: B, BamHI; K, KpnI; N, NheI; S, SpeI; and X, XhoI. A novel BamHI site is introduced into the PXR locus by the homologous recombination event allowing the targeted locus to be distinguished from the wild-type allele by Southern analysis of BamHI digested DNA with the indicated probe (shown at the right). (B) Northern blot analysis of RNA isolated from the livers of wild-type and PXR−/− mice by using the probes indicated in the schematic of the PXR cDNA. Reverse transcription (RT)–PCR was performed using the primers indicated in the schematic. Amplification of the wild-type and disrupted PXR mRNAs yielded products of 111 bp and 363 bp, respectively. (C) Total RNA was prepared from the livers of three wild-type and PXR−/− mice treated with PCN, PB, dexamethasone, or vehicle alone. RNA samples were pooled before Northern blot analysis with probes for Cyp3a11. Bands were quantitated as described in Materials and Methods and represent the mean obtained from three animals in each treatment group. Values are normalized to β-actin and are expressed as fold change relative to wild-type mice receiving vehicle alone.