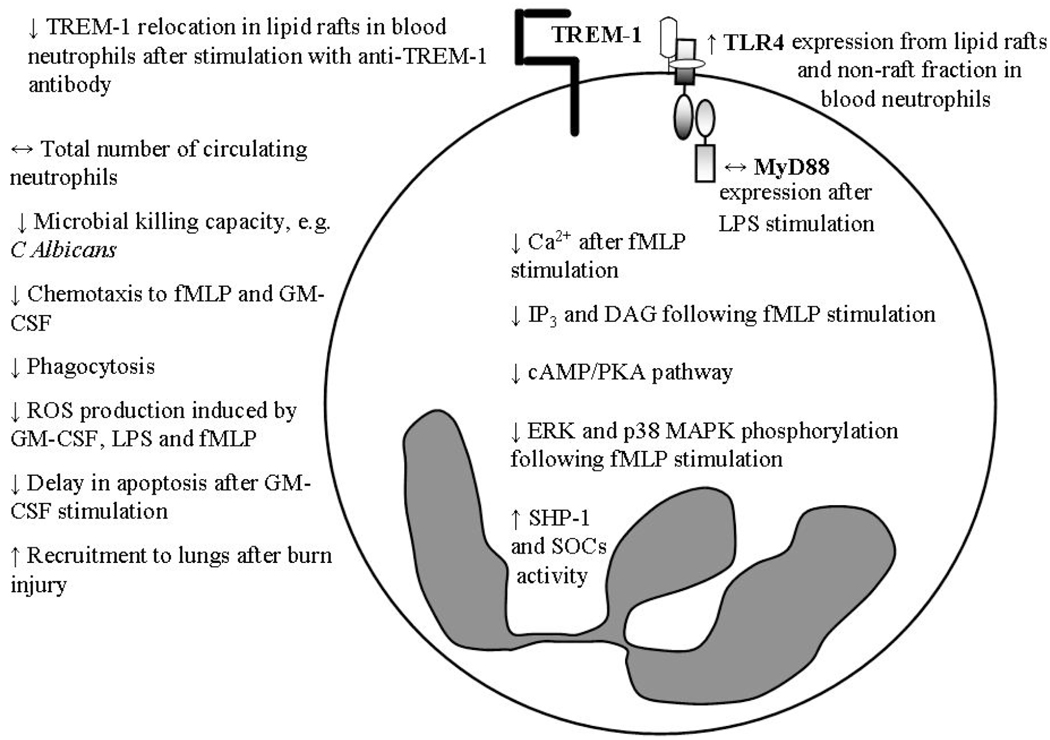
Fig. (1).
Neutrophil defects with advanced age. Arrows (↑, ↓ or ↔) denote increased, decreased or unaltered levels in the aged compared to the young. Abbreviations: fMLP, N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine; GM-CSF, granulocyte monocyte colony stimulating factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TREM-1, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cell-1, TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; MyD88, Myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88); IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; DAG, diacyl glycerol; cAMP/PKA, cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; SHP-1, inhibitor of Src family of tyrosine kinases, SOCs, suppressors of cytokine signaling.