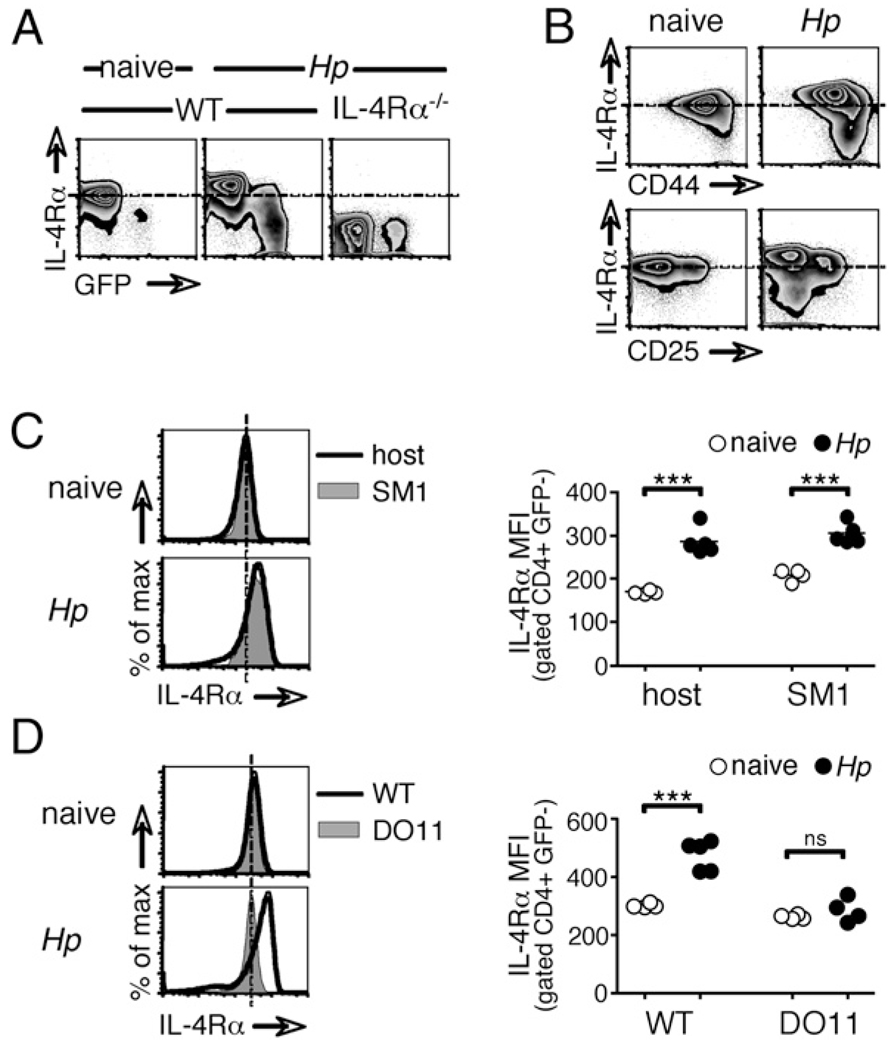
FIGURE 2.
Modulation of IL-4Rα expression upon infection with a helminth parasite. A, WT and IL-4Rα−/− 4get reporter mice, in which GFP fluorescence denotes IL-4 expression, were infected with H. polygyrus for 14 d. mesLN cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Data shown are gated on CD4+ cells. B, WT mice were infected and analyzed as in A. C, CD4+ cells from SM1 TCR transgenic mice on a RAG−/− background, which are specific for an irrelevant Salmonella Ag, were transferred into congenically distinct, WT recipients 13 d after H. polygyrus infection. Twenty-four hours later, mesLN CD4+ cells of donor and recipient origins were analyzed for their expression of IL-4Rα by flow cytometry. D, WT BALB/c or DO11.10 TCR transgenic mice, in which T cells recognize only OVA were infected with H. polygyrus, and 14 d later, CD4+ cells from mesLNs were analyzed by flow cytometry. Data in all of the panels are representative of two or more independent experiments.