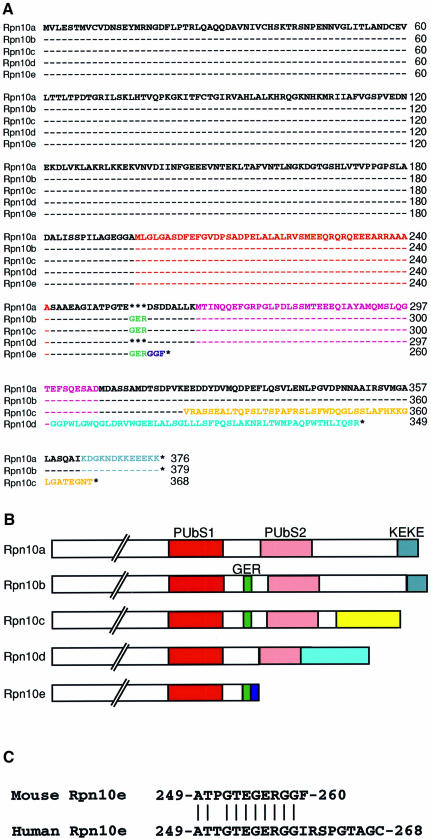
Fig. 1. A family of mouse Rpn10 proteins. (A) Sequence alignment of the Rpn10 proteins deduced from the cDNA sequences. The multi-Ub-binding domains [PUbS1 (red) and PUbS2 (pink)], the Gly-Glu-Arg (GER) sequence (green), the KEKE domain (gray) and the specific C-terminal sequences in Rpn10c (yellow), Rpn10d (pale blue) and Rpn10e (dark blue) are indicated by colored letters. Dashes indicate identical amino acid residues, and asterisks indicate absence of residues. (B) Schematic representation of the C-terminal half structures of multiple Rpn10 proteins. The amino acid sequences written in color in (A) are shown as boxes of the same color. (C) C-terminal sequence alignment of the mouse and human Rpn10e deduced from the cDNA sequences. Vertical bars indicate identical amino acids. Numbers on the right indicate the residue numbers of the C-terminal amino acids. Note that the regions not shown are identical between the mouse and human Rpn10e.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.