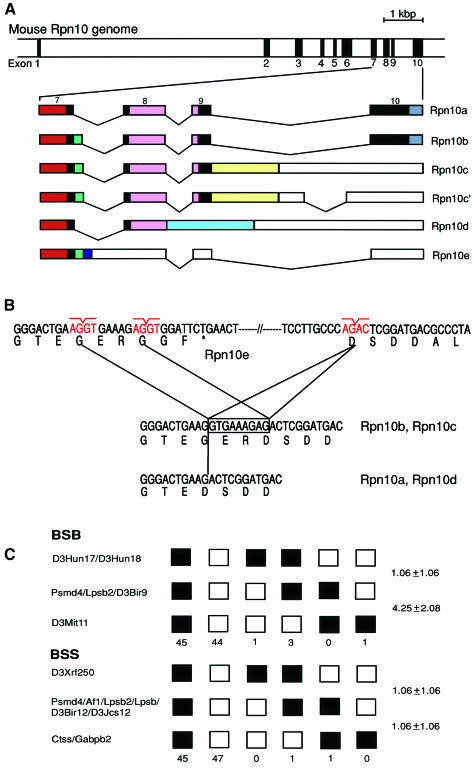
Fig. 2. Genomic organization and chromosomal localization of the mouse Rpn10 (Psmd4) gene. (A) Physical map of the Rpn10 gene. Exons are indicated by filled boxes and numbered from 1 to 10 (upper panel). The structures of multiple Rpn10 mRNAs generated by alternative splicing are shown schematically. Solid and open boxes indicate the coding region and the 3′-untranslated region, respectively (lower panel). Colored boxes correspond to those of the same color in Figure 1B. Rpn10c and Rpn10c′ code for an identical protein. (B) Differential usage of the splice donor sites in intron 7 accounts for the presence or absence of the Gly-Glu-Arg sequence. An asterisk in Rpn10e indicates a termination codon. (C) Mapping of the Rpn10 gene to chromosome 3. The sequences of the primers used for PCR were 5′-GGGAACAGAGTTTAGCCAAGAATCG-3′ and 5′-TGACGTCATAGTCATCCTCCTC-3′. In BSB, open boxes represent the C57BL/6J-M.spretus heterozygote pattern, and closed boxes the homozygous C57BL/6J pattern. In BSS, open boxes represent the homozygous SPRET/Ei pattern, and closed boxes the C57BL/6Ei-SPRET/Ei heterozygote pattern. The number of mice carrying each type of chromosome is shown below the boxes. For each panel, 94 animals were typed. Recombination frequencies between pairs of loci (percentage recombination with standard errors) are given at the right side. The loci not separated by recombination are indicated by ‘/’.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.