Figure 2.
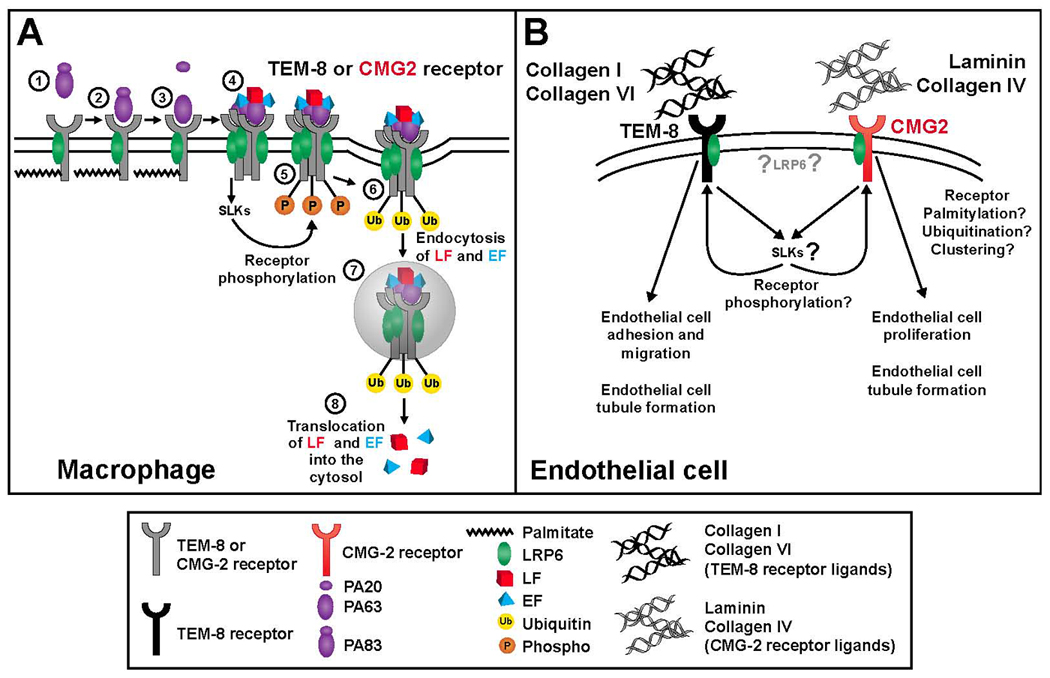
Facilitation of cellular anthrax toxin entry (A) and angiogenesis (B) by the anthrax toxin receptors. A. Entry of anthax toxin into macrophages. 1. PA binds to the palmitoylated and LRP6 bound macrophage cell anthrax receptors (TEM-8 or CMG-2). 2. PA is cleaved by furin like proteases with PA63 remaining bound to the receptor. 3. Clustering of anthrax toxin receptors and forming of a heptameric prepore induces src like kinase (SLK) signaling and binding of lethal toxin (LT) and edema toxin (ET) to the receptors. 4. SLK activation leads to phosphorylation of anthrax receptors. 5. Phosphorylation of anthrax receptors leads to ubiquitination of the receptors. 6. Endocytosis of LT and ET along with the receptors. 7. LT and ET are released into the cytoplasm. B. Putative functions of the anthrax receptors in angiogenesis. TEM-8 is known to bind to collagen I and collagen VI while CMG-2 binds to collagen IV and laminin. TEM-8 is thought to be involved in the regulation of endothelial cell migration and CMG-2 is proposed to regulate both endothelial cell proliferation and tubule formation. The influence of LRP6, SLK signaling, and anthrax receptor phosphorylation, palmitoylation, ubiquitination, and clustering, on these angiogenic functions in endothelial cells remains to be determined.
