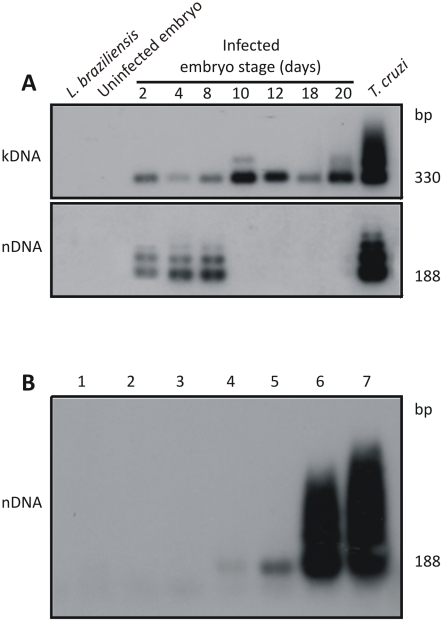
Figure 1. Elimination of Trypanosoma cruzi infection early in Gallus gallus embryonic development.
A) Top panel shows 330 bp bands formed by PCR amplified minicircles kDNA templates harvested at several stages of the chicken embryonic development, after hybridization with a specific probe; Bottom panel shows bands formed by PCR amplified from same embryos after separation in 1% agarose gel and hybridization with a specific nDNA probe; the 188 bp nDNA band was diagnostic of the parasite persistence in the host tissue. B) Sensitivity of the PCR with nDNA primers Tcz1/2. Lanes 1 and 2, control DNA from kDNA negative and from kDNA-mutated chickens; Lanes 3 to 7, mix of 200 ng of control chicken DNA with increasing amounts of T. cruzi DNA, respectively: 1 fg, 10 fg, 1 pg, and 100 pg, and 1 ng. The hybridization with the radiolabeled 188-bp probe improved the technique sensitivity (10 fg), which reached 24-fold below the diploid T. cruzi total DNA.