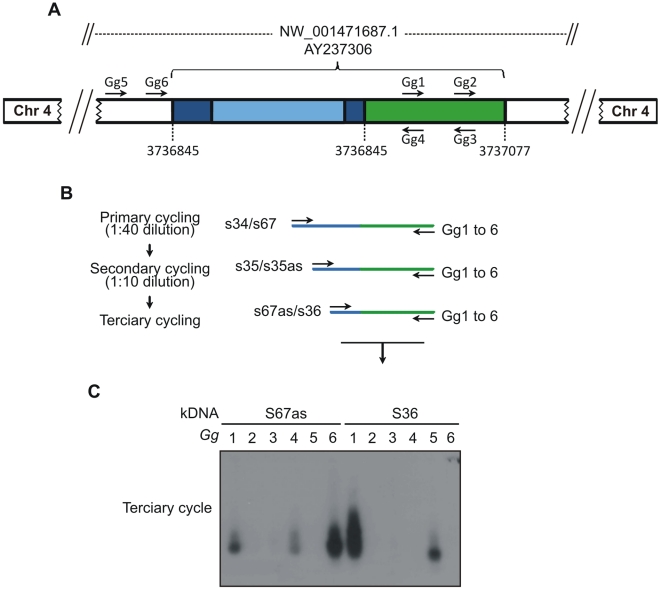
Figure 4. The tpTAIL-PCR strategy used to detect Trypanosoma cruzi kDNA integration into the Gallus gallus genome.
A) A chimera sequence with a fragment of kDNA minicircle conserved (dark blue) and variable (light blue) regions integrated in the locus NW_001471687.1 at chromosome 4 (AY237306) of the chicken genome (green) was used to obtain the host specific primer sets (Gg1 to Gg6). B) The tpTAIL-PCR amplifications were initiated (primary cycle) by annealing of the kDNA-specific S34 or S67 primers in combination with chicken-specific Gg1 to Gg 6 primers. Diluted products provided template for the secondary cycle with the S35 (sense/antisense) primers and the combinations of Gg primers. In the tertiary cycle a dilution of the secondary products was subjected to amplification with kDNA S36 or S67 antisense primers in combination with the Gg primers. C) These amplification products were separated in 1% agarose gels and transferred to nylon membrane, hybridized with the specific kDNA probe, then cloned and sequenced. The combinations of kDNA and targeted Gg1 to Gg6 are shown on top of the gel. The sequential PCR reactions amplified target kDNA-host DNA sequences with kDNA minicircles (blue) and the avian sequence (green).