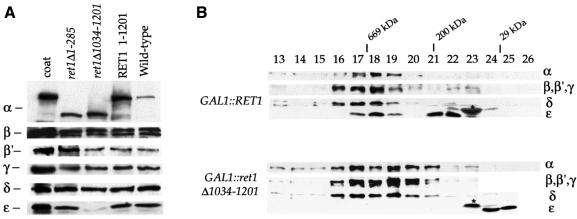
Fig. 4. (A) ε-COP levels are severely reduced in ret1Δ1034–1201 mutant cells. ret1Δ strains expressing full-length α-COP (RET1) or the α-COP truncations (ret1Δ1–285 or ret1Δ1034–1201) from a CEN plasmid under the control of the GAL1 promoter, as well as a congenic wild-type control were grown to log phase at 30°C. Total cell extracts were analysed by immunoblotting. α-COP was detetected with anti-coatomer antiserum; the other COPs were detected with subunit-specific antisera. Note the higher levels of GAL1-overexpressed α-COP compared with wild-type cells, as expected, and the size differences between full-length and truncated α-COP. Further, note the dramatic depletion of ε-COP in ret1Δ1034–1201 cells, and comparable levels of β-, β′-, γ- and δ-COP in all four strains. (B) In ret1Δ1034–1201 mutant cells, ε-COP is not bound to coatomer. Superose 6 gel filtration of cytosolic proteins from GAL1::RET1 cells and GAL1::ret1Δ1034–1201 cells. SDS–PAGE-separated proteins of column fractions were probed with anti-coatomer antiserum to detect α-COP, β′-, β-, γ-COP (which co-migrate as a triplet) and δ-COP; an anti-ε-COP serum was used to detect ε-COP; the asterisk marks a non-specific, cross-reactive band. To visualize the reduced amounts of ε-COP in GAL1::ret1Δ1034–1201 cells, the ε-COP lane required longer exposure than for GAL1::RET1 cells. Note that coatomer from GAL1::RET1 cells elutes with a molecular mass of 700–800 kDa (fractions 17 + 18), similar to coatomer from wild-type cells (Duden et al., 1998), and that ε-COP co-fractionates with coatomer. Additional ε-COP is present in a prominent peak (∼200 kDa), most likely containing proteolytic fragments of the overexpressed, monomeric α-COP not detectable with anti-coatomer serum (fractions 21 + 22). Note that in GAL1::ret1Δ1034–1201 cells, ε-COP is absent from the broad coatomer peak around fractions 17–20. ε-COP is present exclusively in low molecular weight fractions in monomeric form. Fraction numbers and positions of marker proteins are indicated: thyroglobulin (669 000), β-amylase (200 000) and carboanhydrase (29 000).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.