Figure 4. HCV infection induces HCV-specific human T cell response in AFC8-hu mice.
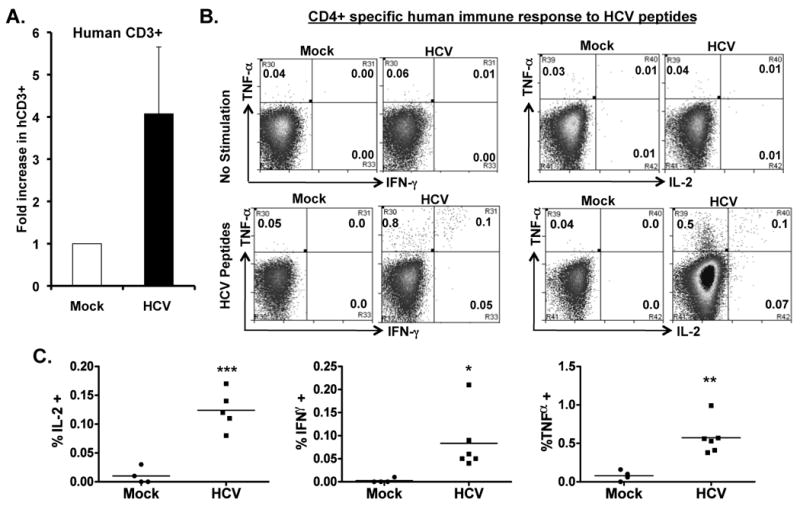
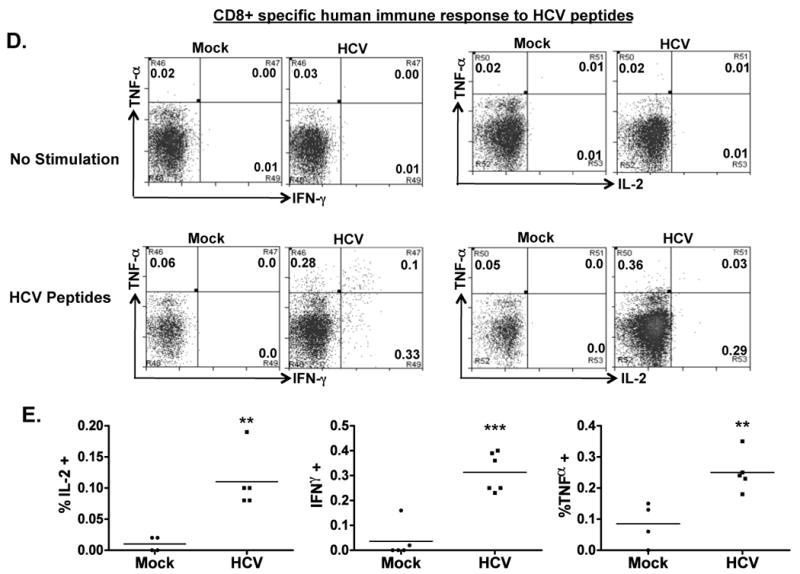
(A) Preferential expansion of human T cells from HCV-infected AFC8-hu mice after stimulation with HCV Core peptides. Spleen and LN cells from mock and HCV-infected AFC8-hu mice were stimulated with a pool of HCV Core peptides + anti-CD28 mAb, and cultured for 8-10 days. Fold increase of human CD45+CD3+ cells from HCV infected samples (n=4) was calculated relative to mock samples (n=3). P <.05. (B-E) The expanded T cells were re-stimulated with HCV peptides and stained for intracellular human cytokines (IL-2, IFN-γ and TNF-α). (B) Human CD4+ T cells are analyzed for expression of the cytokines. No stimulation controls show background. (C) Summarized results of individual mice are shown. (D) Human CD8+ T cells are analyzed for expression of the cytokines. Representative FACS plots are shown for each cell population. Numbers in FACS plots represent the % cytokine+ of CD4 or CD8 T cells. (E) Shown are summarized data of individual mice from two cohorts of mice (n = 4 per group). Lines indicate the mean values. *, P <.05; **, P <.01; ***, P < .001.
