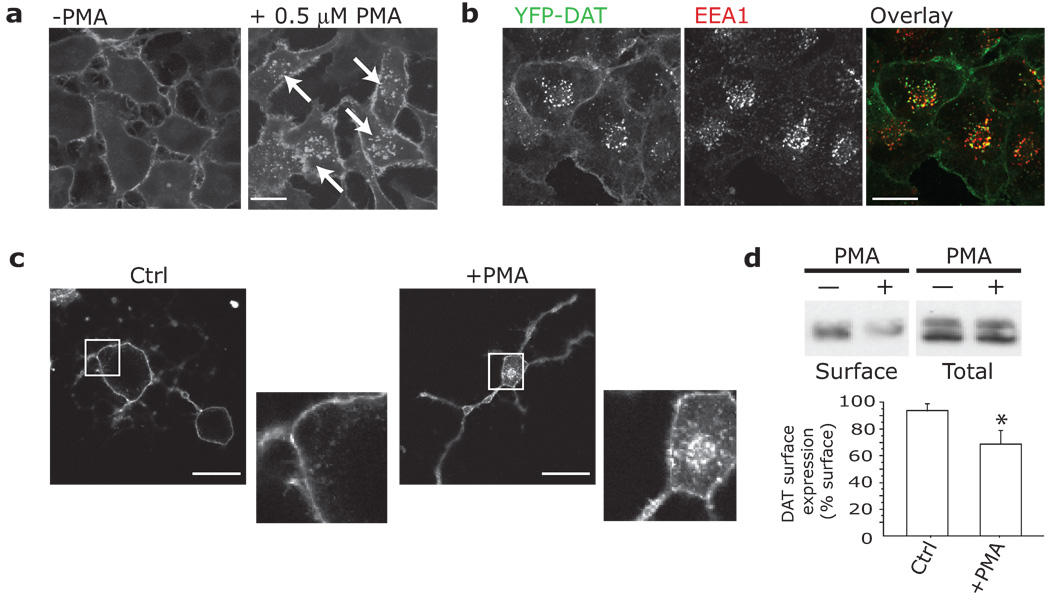
Fig.1. PKC triggers endocytosis of heterologously and endogenously expressed DAT.
a,b. EM4-YFP-DAT internalizes (white arrows) into EEA1-positive vesicles after exposure to 0.1 µM PMA for 30 min. Cells exposed to PMA were fixed and immunostained for EEA1 as described. Alexa-Fluor 633 labeled secondary antibodies were used to prevent overlap with YFP. Scale bar = 10 µm. c. Endogenous DAT internalizes in response to PMA in primary dopaminergic neurons. Midbrain cultures were treated with vehicle (Ctrl, n = 32) or 1 µM PMA (+PMA, n = 35) for 30 min, fixed and immunostained for DAT (intracellular epitope, Chemicon), and Alexa-Fluor 568 secondary. PMA led to significant internalization of DAT (‘Internalization Index,’ as described in Methods, Ctrl: 0.076±0.013; vs. PMA: 0.309±0.052). (One-way ANOVA; p < 0.001). Scale bar = 20 µm. d. Internalization of endogenous DAT in striatal slice preparations (n = 6). Slices were treated with 10 µM PMA or Ctrl for 1 hr, then cell surface biotinylated to determine DAT surface levels. ‘DAT expression levels (% Surface)’ indicates the relative amount of DAT at the cell surface, and was calculated as the ratio between the integrated densities of the surface levels of DAT after treatment (corrected for total levels of DAT) to the surface levels of DAT before treatment (corrected for total levels of DAT). Bars represent Mean + St. Dev. PMA treatment significantly decreased DAT surface levels (p = 0.0330). Complete blots can be found in Figure S9.