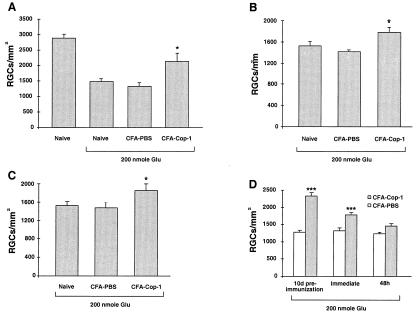
Figure 4.
Neuroprotection from glutamate toxicity by active immunization with Cop-1. (A) Ten days before glutamate injection, mice were immunized by s.c. injection with Cop-1 in CFA (5 mg/ml bacteria) or injected with PBS in CFA. The results of one experiment are shown (n = 5 in each group). The number of surviving RGCs per square millimeter (mean ± SEM) was significantly higher in the Cop-1-immunized mice than in the mice injected with PBS in CFA or in mice that received glutamate only (P < 0.02, two-tailed t test). Injection with PBS in CFA had no detectable effect on the number of RGCs. The experiment was repeated three times, with identical results. Altogether 13 animals in the Cop-1-treated group and 15 animals in the PBS-treated group were tested. (B) Immediately after intravitreal injection of glutamate, mice were immunized with Cop-1 emulsified in CFA (5 mg/ml bacteria). The number of surviving RGCs per square millimeter (mean ± SEM) was determined 1 week later. The results of one experiment are shown. The effect of immunization with Cop-1 was significant (P < 0.05; two-tailed t test; n = 12 for Cop-1 and n = 8 for the control). This experiment was repeated with 11 mice for Cop-1 immunization and eight mice for injection with PBS in CFA (5 mg/ml bacteria). (C) RGC survival after glutamate insult and immediate immunization with Cop-1 in adjuvant containing 0.5 mg/ml of bacteria. The number of surviving RGCs per square millimeter was significantly higher in the Cop-1-immunized mice (n = 15) than in the mice injected with glutamate (n = 5) (P < 0.04; two-tailed t test). (D) Survival of RGCs after immunization performed before, immediately after, or 48 h after glutamate insult. Bars show the pooled results obtained for all mice examined in each treatment, collected from repeated experiments. No effect was seen when immunization was performed 48 h after the insult.