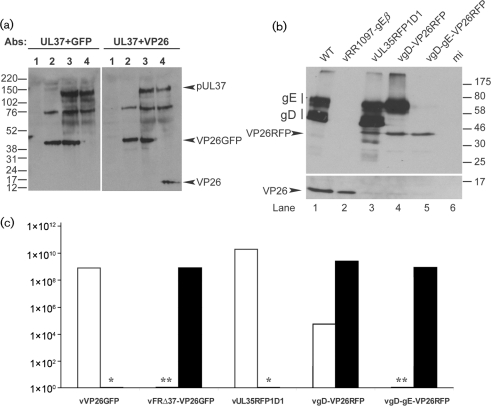
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the vFRΔ37-VP26GFP and vgD-gE-VP26RFP viruses. (a) RS cells were mock-infected (lane 1) or infected with 5 p.f.u. of vFRΔ37-VP26GFP (lane 2), vVP26GFP (lane 3) or WT HSV-1 (lane 4) per cell and harvested after 24 h. Proteins were analysed by Western blotting using the pUL37 antibody, together with either the GFP-specific antibody (left panel) or the VP26-specific antibody (right panel). Note that a viral protein migrating at approximately 75 kDa is recognized non-specifically by the pUL37 antibody. Molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated to the left of the figure. (b) Vero cells were infected with 5 p.f.u. of WT HSV-1 (lane 1), vRR1097-gEβ (lane 2), vUL35RFP1D1 (lane 3), vgD-VP26RFP (lane 4) or vgD-gE-VP26RFP (lane 5) per cell or were mock-infected (lane 6), and harvested after 24 h. Proteins were analysed by Western blotting using a gD antibody, a gE antibody and a VP26-specific antibody. Molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated to the right of the figure. (c) Growth of viruses on complementing (filled bars) and non-complementing (empty bars) cell lines. Concentrated stocks of virus were titrated on RS cells (vVP26GFP), Vero cells (vUL35RFP1D1, vgD-VP26RFP, vgD-gE-VP26RFP), 80C02 cells [a clone of RS cells expressing UL37 (Roberts et al., 2009)] (vFRΔ37-VP26GFP) or VD60 cells [a clone of Vero cells expressing gD (Ligas & Johnson, 1988)] (vgD-VP26RFP, vgD-gE-VP26RFP). *vVP26GFP and vUL35RFP1D1 were not tested on complementing cells. **The titres of vFRΔ37-VP26GFP and vgD-gE-VP26RFP on non-complementing cells were assigned as <103 because the input virus caused severe cytopathic effects at lower dilutions.