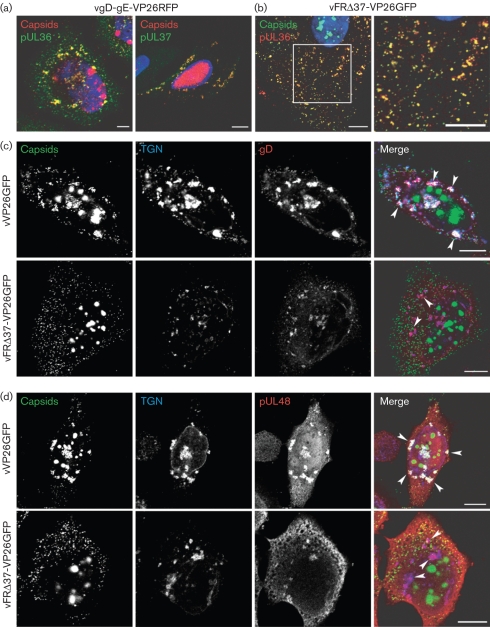
Fig. 3.
Effect of UL37 and gD–gE deletions on the localization of glycoproteins and tegument proteins. (a) HeLa cells infected with vgD-gE-VP26RFP for 15 h were fixed and labelled with the anti-pUL36 antibody and a GAM633 antibody (pseudo-coloured in green) or were permeabilized with digitonin and labelled with anti-pUL37 antibody and a GARCy5 antibody (pseudo-coloured in green) under native conditions as described by Copeland et al. (2009). Bar, 5 μm. (b) HeLa cells were infected with vFRΔ37-VP26GFP for 15 h, fixed and labelled with anti-pUL36 antibody and a GAR568 antibody (red). (c) HeLa cells were infected with 5 p.f.u. of vVP26GFP or vFRΔ37-VP26GFP per cell. At 15 h post-infection, cells were fixed and labelled with TGN46-specific antibody and a GARCy5 antibody to label the TGN (blue), and with a gD-specific antibody and a GAM568 antibody to label gD (red). Capsids were visualized through direct GFP fluorescence (green). (d) Cells were infected and treated as in (c) except that the gD-specific antibody was replaced by pUL48-specific antibody to label pUL48 (red). Arrowheads in (c) and (d) indicate the positions of some TGN-derived vesicles. Bars, 10 μm.