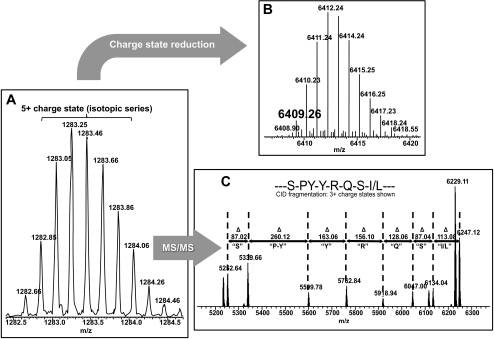
Figure 7.
Workflow for top-down–directed protein identification on a 7-T LTQ FT-ICR mass spectrometer. (A) Initially, an isotopic distribution of a single charge state (here, [M+5H+]5+) for a given protein species is measured in the ICR cell of the mass spectrometer, to obtain a high-resolution spectrum. (B) This spectrum is then computationally deconvoluted into its [M+H+]1+ isotopic distribution, to determine its true mass (here, 6409.26 Da) for database comparison. (C) The [M+5H]5+ ion is subjected to collision-induced dissociation in the ion trap (LTQ), causing fragmentation through collision with an inert gas where the excess kinetic energy of the ion is converted into peptide-bond breaking potential energy resulting in fragment ions to be measured in the high-resolution ICR cell. These data give a partial sequence of the selected precursor ion for database comparison.