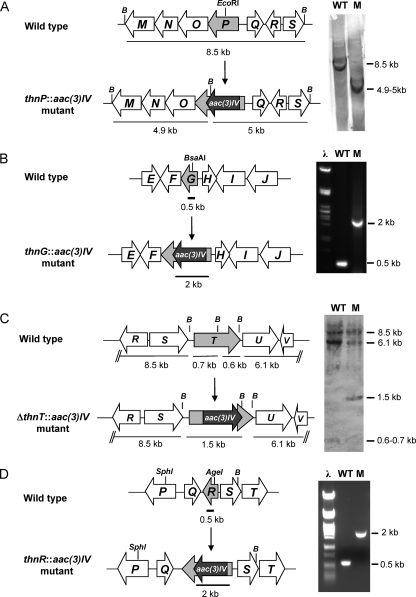
FIG. 2.
Generation of mutants in thn genes. Shown are the organizations of chromosomal regions of the wild type and the mutant strains and genetic analysis by Southern analysis (A and C) and by PCR (B and D). Only relevant restriction sites are indicated, and B indicates BamHI. The gray arrow represents the mutated gene, and the black arrow indicates the aac(3)IV gene, encoding the apramycin resistance marker (apr cassette). (A) Insertion of the apr cassette into the thnP coding region and Southern hybridization of BamHI-digested genomic DNA from the wild type (WT) and the thnP::aac(3)IV mutant (M) using the 8.5-kb BamHI fragment as a probe. (B) Insertion of the apr cassette into the thnG coding region and PCR analysis of genomic DNA from the wild type and the thnP::aac(3)IV mutant using oligonucleotides ThnG-R and ThnG-F. (C) Deletion of the internal fragment of thnT and replacement with the apr cassette (see Materials and Methods) and Southern hybridization of BamHI-digested genomic DNA from the wild type and the ΔthnT::aac(3)IV mutant using pHZMRT as a probe. (D) Insertion of the apr cassette into the thnR coding region and PCR analysis of genomic DNA from the wild type and the thnR::aac(3)IV mutant using oligonucleotides ThnR-R and ThnR-F.