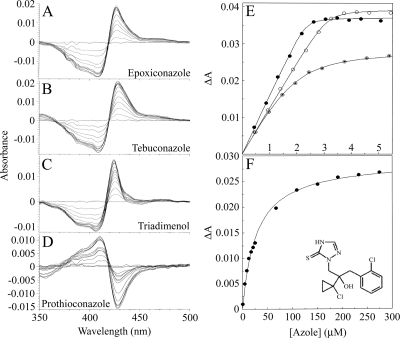
FIG. 2.
Binding properties of azole fungicides to MgCYP51. Epoxiconazole (A), tebuconazole (B), triadimenol (C), and prothioconazole (D) bound to 4 μM MgCYP51. Each line represents the successive addition of antifungal, resulting in a progressive increase in absorbance at 423 to 429 nm and a decrease in absorbance at 406 to 409 nm with epoxiconazole, tebuconazole, and triadimenol and a progressive increase in absorbance at 410 nm and decrease in absorbance at 428 nm with prothioconazole, until saturation is reached. (E) The concentration of azole added to MgCYP51 and the resulting change in absorbance (ΔApeak-trough) were plotted to produce binding saturation profiles for epoxiconazole (•), tebuconazole (○), and triadimenol (⊙) using the Morrison equation. (F) A prothioconazole saturation profile was constructed by using the Michaelis-Menten equation. The data for one of three replicates are shown. The chemical structure of prothioconazole is also shown in panel F.