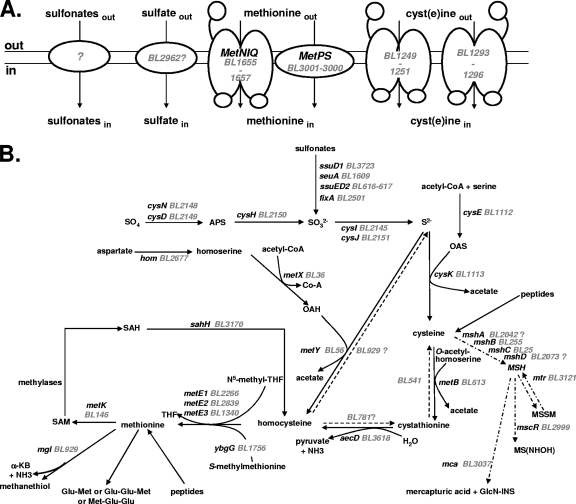
FIG. 1.
Sulfur metabolism in B. aurantiacum. The BL numbers for B. aurantiacum genes correspond to those of Agmial (http://genome.jouy.inra.fr/∼vloux/publications/forquin08/) (8). A systematic search for E. coli, B. subtilis, C. glutamicum, and M. tuberculosis genes involved in sulfur metabolism was performed. The high-GC-content Gram-positive bacteria C. glutamicum and M. tuberculosis are phylogenetically related to Brevibacterium strains (33, 49). The genes were renamed according to B. subtilis and C. glutamicum orthologues. “?” indicates a step or a pathway for which the gene proposed remains to be more clearly identified. (A) Transport of sulfur compounds. Methionine transporters (MetNIQ, MetPS), cyst(e)ine transporters (BL1249 to BL1251, BL1293 to BL1296), sulfate transporters and sulfonate transporters are indicated. (B) Central sulfur metabolism. ATP sulfurylase, cysDN; APS reductase, cysH; sulfite reductase, cysJI; serine O-acetyltransferase, cysE; OAS thiol-lyase, cysK; homoserine dehydrogenase, hom; homoserine acetyl-transferase, metX; OAH thiol-lyase, metY; cystathionine β-lyase, aecD; cystathionine γ-synthase, metB; methionine synthase, metE1-3; methionine γ-lyase, mgl; SAM synthetase, metK; SAH hydrolase, sahH; alkanesulfonate monooxygenase, ssuD1-2; flavin mononucleotide (FMN) reductase, ssuI; FMNH2-dependent alkanesulfonate monooxygenase, seuA; electron transfer flavoprotein, fixA; glycosyltransferase, mshA; MSH deacetylase, mshB; MSH ligase, mshC; MSH synthase, mshD; MSH disulfide reductase, mtr; NAD/mycothiol-dependent formaldehyde dehydrogenase/nitrosothiol reductase, mscR; MSH-S-conjugate amidase, mca; Ac-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A; APS, adenylyl sulfate; PPi, diphosphate; OAS, O-acetylserine; OAH, O-acetylhomoserine; MSH, mycothiol; MSSM, mycothiol disulfide; GlcN-INS, glucoaminonylinositol; THF, tetrahydrofolate; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; α-KB, α-ketobutyrate.