FIG. 3.
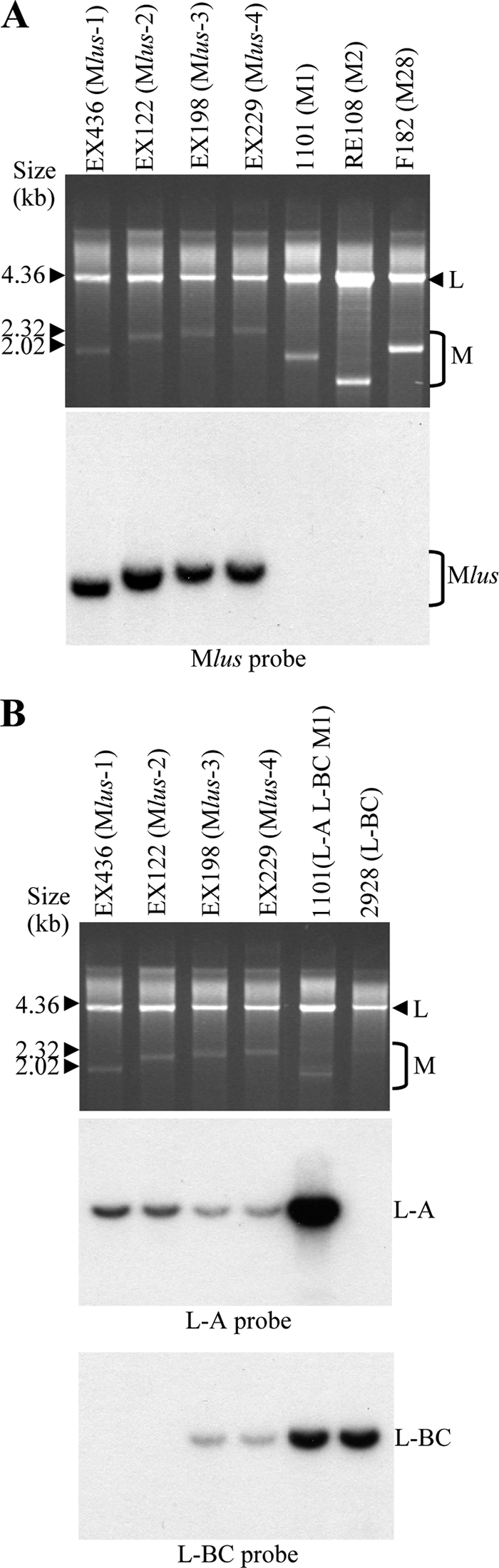
Characterization of the Klus yeast dsRNAs. (A) Mlus is different from M1, M2, or M28 dsRNAs. Nucleic acids from killer yeasts K1 (1101), K2 (RE108), and K28 (F182) or from the four Klus isotypes (EX436, EX122, EX198, and EX229) were separated on an agarose gel. (Top) Ethidium bromide staining of the gel; (bottom) Northern hybridization with a Mlus probe. (B) Presence of L-A and L-BC dsRNAs in Klus strains. Total nucleic acids from the same Klus strains shown in panel A and from standard laboratory strains 1101 (L-A, L-BC, and M1) and 2928 (L-BC) were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis (top; ethidium bromide staining of the gel). The RNA molecules were blotted onto a nylon membrane and hybridized with specific probes for L-A (middle) or for L-BC (bottom). Τhe size markers correspond to lambda DNA digested with HindIII.
