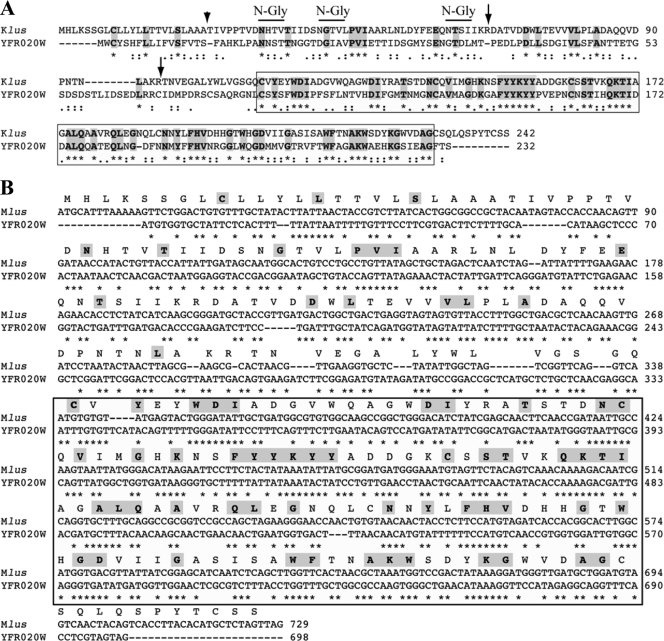
FIG. 7.
Relationship between Mlus and YFR020W protein. (A) Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the Klus putative preprotoxin and the YFR020W ORF protein. The comparison was done using the ClustalW multiple sequence alignment program (41). Asterisks (*) indicate identical amino acids; double dots (:) and single dots (.) indicate conserved and semiconserved substitutions of amino acids, respectively. Identical amino acids are also marked in bold and shaded. The C-terminal 117-amino-acid region that displays a 44.4% identity between both proteins is boxed. The short arrow indicates the putative processing site, after the signal peptide. Long arrows indicate the location of putative Kex2 endopeptidase sites, after KR amino acids. Potential N-glycosylation sites are marked by overlining of the respective sequences. (B) Comparison of the nucleotide sequences of the Klus ORF and the YFR020W ORF. The comparison was done using ClustalW as described in the legend to panel A. The Klus ORF protein amino acid sequence is displayed above the nucleotide sequence. In bold and shaded are the amino acids identical to those of the YFR020W protein. Note that in the boxed area, the unchanged amino acids are coded for either by identical triplets or by triplets in which the first and second nucleotides are identical and the third (wobble position) is modified.