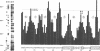Abstract
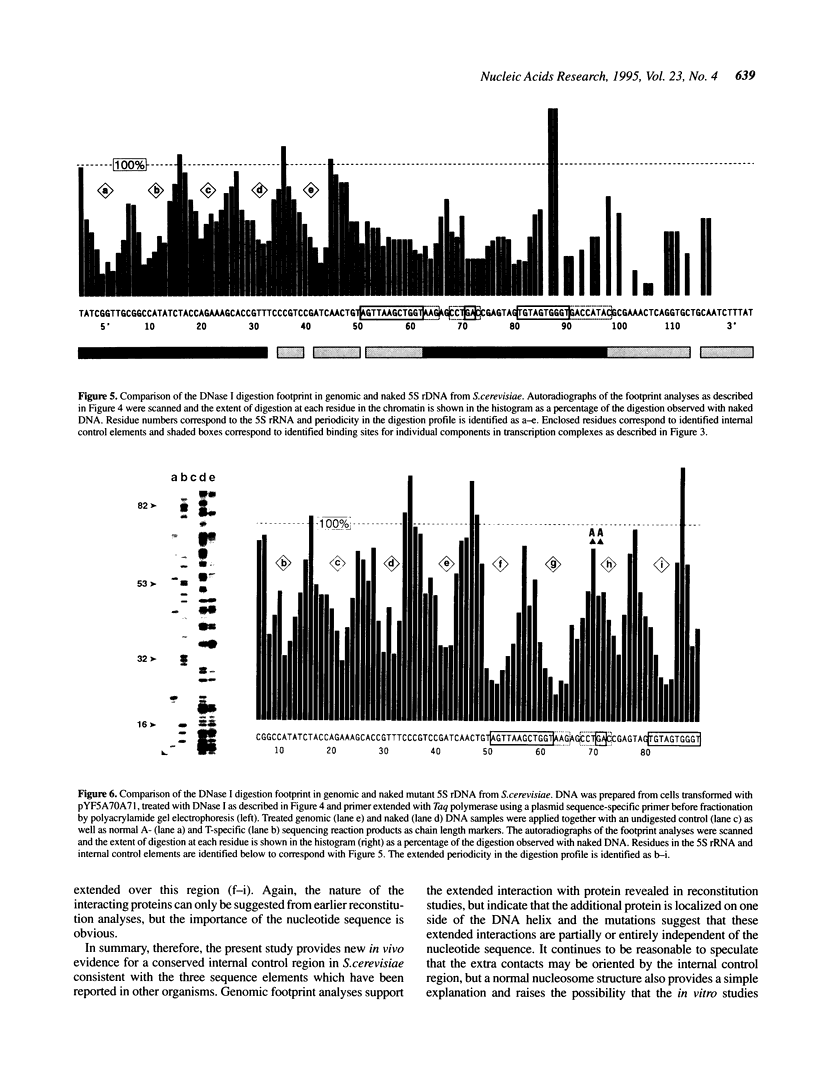
The internal control region of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5S rRNA gene has been characterized in vivo by genomic DNase I footprinting and by mutational analyses using base substitutions, deletions or insertions. A high copy shuttle vector was used to efficiently express mutant 5S rRNA genes in vivo and isotope labelling kinetics were used to distinguish impeded gene expression from nascent RNA degradation. In contrast to mutational studies in reconstituted systems, the analyses describe promoter elements which closely resemble the three distinct sequence elements that have been observed in Xenopus laevis 5S rRNA. The results indicate a more highly conserved structure than previously reported with reconstituted systems and suggest that the saturated conditions which are used in reconstitution studies mask sequence dependence which may be physiologically significant. Footprint analyses support the extended region of protein interaction which has recently been observed in some reconstituted systems, but mutational analyses indicate that these interactions are not sequence specific. Periodicity in the footprint provides further detail regarding the in vivo topology of the interacting protein.
Full text
PDF



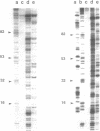
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew B., Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Geiduschek E. P. The subunit structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor IIIC probed with a novel photocrosslinking reagent. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2197–2205. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07389.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun B. R., Bartholomew B., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Topography of transcription factor complexes on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5 S RNA gene. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 20;228(4):1063–1077. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90315-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun B. R., Riggs D. L., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Multiple states of protein-DNA interaction in the assembly of transcription complexes on Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2530–2534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challice J. M., Segall J. Transcription of the 5 S rRNA gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires a promoter element at +1 and a 14-base pair internal control region. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20060–20067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipev C. C., Wolffe A. P. Chromosomal organization of Xenopus laevis oocyte and somatic 5S rRNA genes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H. Protein-DNA interactions at a yeast replication origin. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):169–172. doi: 10.1038/357169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielsen O. S., Marzouki N., Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Two polypeptide chains in yeast transcription factor tau interact with DNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7505–7511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. D., O'Connell A. M., Sharp S. J. Formation of an active transcription complex in the Drosophila melanogaster 5S RNA gene is dependent on an upstream region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2046–2051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good L., Nazar R. N. An improved thermal cycle for two-step PCR-based targeted mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4934–4934. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R. Direct sequence and footprint analysis of yeast DNA by primer extension. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:550–562. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94042-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. L., Wilson S. L. Identification of a 150-kilodalton polypeptide that copurifies with yeast TFIIIC and binds specifically to tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2018–2024. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Bartholomew B., Blanco J. A., Johnson T. E., Geiduschek E. P. Two essential components of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor TFIIIB: transcription and DNA-binding properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7308–7312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Joazeiro C. A., Pisano M., Geiduschek E. P., Colbert T., Hahn S., Blanco J. A. The role of the TATA-binding protein in the assembly and function of the multisubunit yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor, TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Partial purification and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor TFIIIB. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2819–2827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N. Higher order structure of the ribosomal 5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4562–4567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Van Ryk D. I., Lee Y., Guyer C. D. Use of mutant RNAs in studies on yeast 5S rRNA structure and function. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;69(4):217–222. doi: 10.1139/o91-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Nucleotide sequence of 5 S RNA from Torulopsis utilis. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 15;40(1):106–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80904-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M. C., Weil P. A. Purification and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor TFIIIC. Polypeptide composition defined with polyclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5095–5103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Increased copy number of the 5' end of the SPS2 gene inhibits sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2484–2490. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Structural analysis of a triple complex between the histone octamer, a Xenopus gene for 5S RNA and transcription factor IIIA. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3473–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE W. J., OKAMURA N., BUSCH H. EFFECTS OF THIOACETAMIDE ON THE COMPOSITION AND BIOSYNTHESIS OF NUCLEOLAR AND NUCLEAR RIBONUCLEIC ACID IN RAT LIVER. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1742–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S. J., Garcia A. D. Transcription of the Drosophila melanogaster 5S RNA gene requires an upstream promoter and four intragenic sequence elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1266–1274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. G., Tyler B. M. All internal promoter elements of Neurospora crassa 5 S rRNA and tRNA genes, including the A boxes, are functionally gene-specific. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8015–8019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Wu R. Insertion of a genetic marker into the ribosomal DNA of yeast. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):536–554. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ryk D. I., Lee Y., Nazar R. N. Efficient expression and utilization of mutant 5 S rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8377–8381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ryk D. I., Lee Y., Nazar R. N. Unbalanced ribosome assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing mutant 5 S rRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16177–16181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ryk D. I., Nazar R. N. Effect of sequence mutations on the higher order structure of the yeast 5 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91050-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. K., Weil P. A. Purification and characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor IIIA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1092–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Morse R. H. The transcription complex of the Xenopus somatic 5 S RNA gene. A functional analysis of protein-DNA interactions outside of the internal control region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4592–4599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]