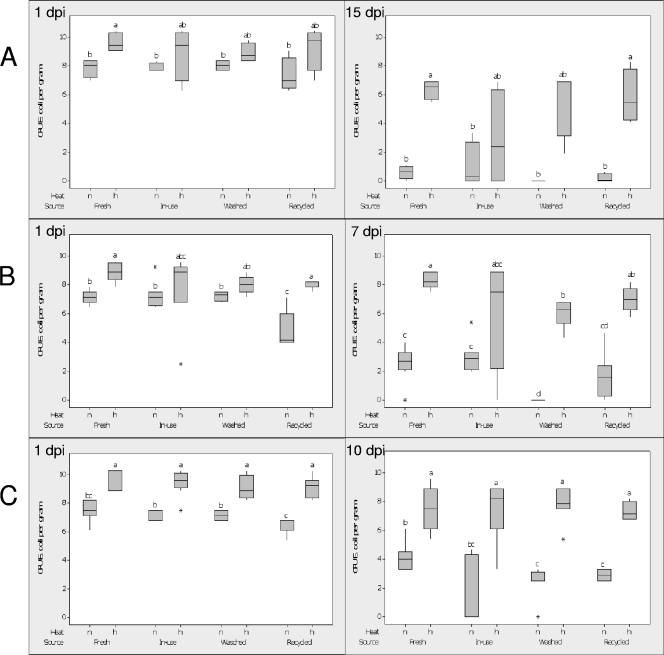
FIG. 1.
Suppression of E. coli O157:H7 in four livestock bedding sources. Bedding samples were acquired on August 2008 (n = 4) (A), November 2008 (n = 8) (B), and March 2009 (n = 8) (C). Sources were as follows: fresh, front of the cow box; in use, back of the cow box; washed, used material from the pile following use of the sand-manure separator; and recycled, rested (≥2 days) pile of washed bedding material. Heat indicates that fresh livestock bedding samples were left either nonheated (n) or heated (h) at 80°C for 30 min to kill off the majority of endogenous microbes before they were subsequently cooled to room temperature. E. coli O157:H7 was then added at 107 CFU g−1 to all samples and incubated at room temperature. The numbers of CFU of E. coli O157:H7 were measured by dilution plating on LB medium amended with ampicillin (50 μg ml−1) and cycloheximide (96 μg ml−1) at 1 dpi or at 7, 10, and 15 dpi. Within each time point, the values for bars indexed with the same letter were not significantly different at P equal to 0.05 when the terminal dilution factors of a 5-fold dilution series were analyzed with Mood's median test. The log-transformed [log10(x)] numbers of CFU of E. coli O157:H7 are presented.