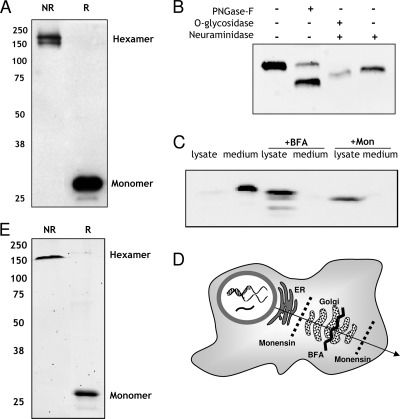
FIG. 2.
BARF1 is secreted as a hexameric glycosylated protein from human HEK293 cells. (A) BARF1 is secreted as a hexamer in the culture supernatant of stably transfected 293HEK-BARF1 cells. Ten microliters of medium was mixed 1:1 with either reduced (R) or nonreduced (NR) loading buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. A 29-kDa and a 160-kDa band can be seen, representing the monomeric and the hexameric structures of sBARF1, respectively. (B) The glycosylation status of BARF1 in serum-free culture supernatant was determined by direct treatment with several glycosidases. PNGase F cleaves high-mannose N-linked sugar groups. Neuraminidase removes sialic acid groups, and O-glycosidase cleaves O-linked sugar chains. The digested protein was loaded on an SDS-PAGE Western blot and detected using 4A6 anti-BARF1 antibody. (C) Manipulation of BARF1 secretion from HEK293 cells. Under normal growth conditions, hardly any BARF1 can be detected in 293HEK cell lysates; BARF1 is completely secreted in the culture supernatant. Treatment of cells with the transport blockers monensin (Mon) and brefeldin A (BFA) retains sBARF1 in the cell lysate and almost completely blocks secretion into the culture medium. (D) Schematic overview of intercellular transport blockage by brefeldin A and monensin. (E) Native-sBARF1 was purified from culture medium using ConA affinity chromatography followed by size exclusion chromatography and visualized by Coomassie staining as hexameric sBARF1 (NR) and monomeric sBARF1 (R). Purity of ∼98% was routinely reached in repeated experiments.