Fig. 1.
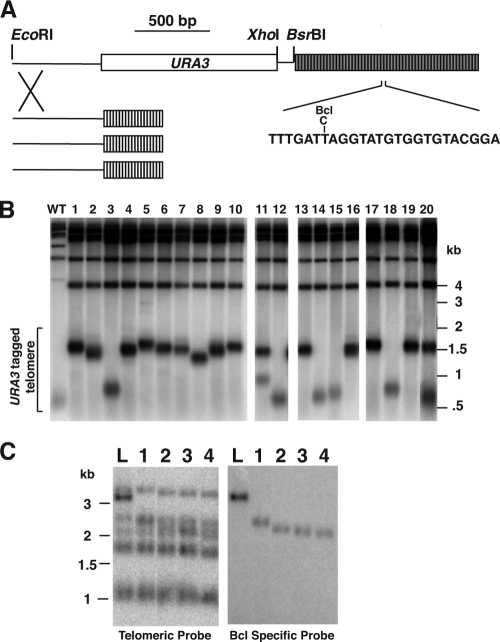
Frequent deletions occur at a long telomere in K. lactis. (A) Diagram of the single long Bcl telomere introduced into K. lactis cells (shown to scale). This telomere contains a URA3 selectable marker gene (white box) inserted into the subtelomeric sequence. The unique XhoI site allows the Bcl telomere to be separated from other telomeres in gels. A native BsrBI site 3 bp internal to the telomere is present in 10 of the 12 wild-type telomeres in the cell. The long telomere is made up completely of Bcl repeats containing a single base pair change that makes a BclI restriction site (gray blocks). After transformation into K. lactis cells with wild-type telomeric repeats (white blocks), the long Bcl telomere recombines via subtelomeric homology and replaces a single native telomere. (B) Southern blot hybridized to a telomeric probe, showing an XhoI digest of genomic DNAs from subclones of cells containing the long Bcl telomere. The wild-type (WT) control is an equivalent telomeric fragment containing a subtelomeric URA3 gene, but of wild-type length and composed of wild-type telomeric repeats. After introduction into K. lactis cells, the XhoI fragment containing the long Bcl telomere measures ∼1.5 kb and contains ∼55 telomeric repeats, indicating that it is ∼3 times longer than a wild-type telomere. The position of the introduced telomere is indicated by the bracket. (C) Southern blot showing an EcoRI digest of telomeres hybridized to the Klac1-25 probe (which hybridizes to both wild-type and Bcl telomeric repeats) and a probe specific for Bcl repeats. Four clones that had undergone TRD are shown (lanes 1 to 4) as well as a clone with the original long telomere (lane L). Markers are shown in kilobases in both panels B and C.