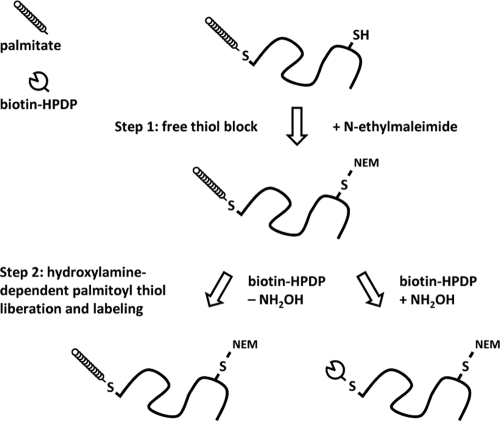
Fig. 4.
Schematic representation of the acyl biotin exchange reaction. Acyl biotin exchange relies on the sensitivity to hydroxylamine (NH2OH) treatment of the covalent thioester linkage between palmitic acid moieties and cysteine residues of protein substrates. In the first step, parasite lysates are treated with N-ethylmaleimide to block reactive free thiols. The sample is then split in half and incubated with the thiol-labeling reagent biotin-HPDP in the presence or absence of NH2OH. Liberation of thiols by NH2OH cleavage enables specific labeling, while the other half of the sample serves as a control for nonspecific labeling due to incomplete preblock, or later, nonspecific purification during streptavidin chromatography.