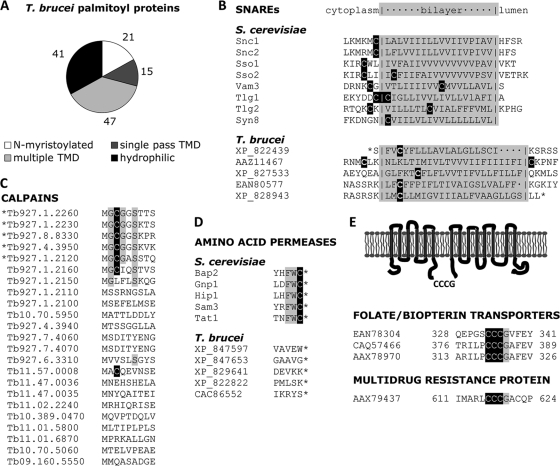
Fig. 6.
Characteristics of T. brucei palmitoyl proteins. (A) Each palmitoyl protein was analyzed for alternative means of membrane association. The proportion belonging to each classification is displayed. (B) As in the yeast proteome, multiple SNAREs with single-pass transmembrane domains were detected. The sequence of the transmembrane domain for each SNARE is displayed with its predicted topology. (C) The N-terminal sequence of each calpain in the T. brucei genome is displayed. Only those calpains sharing a conserved MGCGxxS N terminus were identified in the palmitoyl proteome (indicated with an asterisk). (D) Although several amino acid permeases were identified in the T. brucei palmitoyl proteome, none of them contained the FWC C-terminal tripeptide common to palmitoylated yeast permeases. (E) Three different proteins of the folate/biopterin family were identified as palmitoylated, and each shares a CCCG tetrapeptide in a cytoplasmic loop. Likewise, the multidrug resistance protein A has multiple transmembrane domains and a cytoplasmic CCCG tetrapeptide.