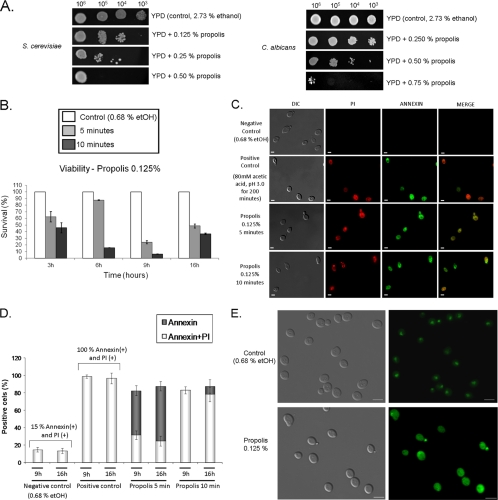
Fig. 1.
Propolis induces apoptosis and late necrosis in S. cerevisiae. (A) Spot dilution assays for S. cerevisiae and C. albicans in YPD medium supplemented with different concentrations of propolis. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 72 h. (B) Viability of yeast cells in different growth cycle phases exposed to 0.125% propolis for 5 or 10 min. Cell viability was determined by plating appropriate cell concentrations and counting the number of colonies. The numbers are the average ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. (C) Annexin and PI assays for 16-h yeast cells exposed to 0.125% propolis. (D) Total numbers for annexin- and PI-positive cells for yeast cells exposed to 0.125% propolis. Bar, 5 μm. The numbers are the average ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. In each experiment, 100 cells were assessed for annexin and PI staining. Positive controls for annexin and PI were exposing the cells to acetic acid, pH 3.0, for 200 min and fixing them with fixation solution as described in the Materials and Methods section. (E) Nucleo-cytosolic translocation of Nhp6Ap-GFP in untreated S. cerevisiae cells or cells exposed to 0.125% propolis for 10 min. Bar, 5 μm.